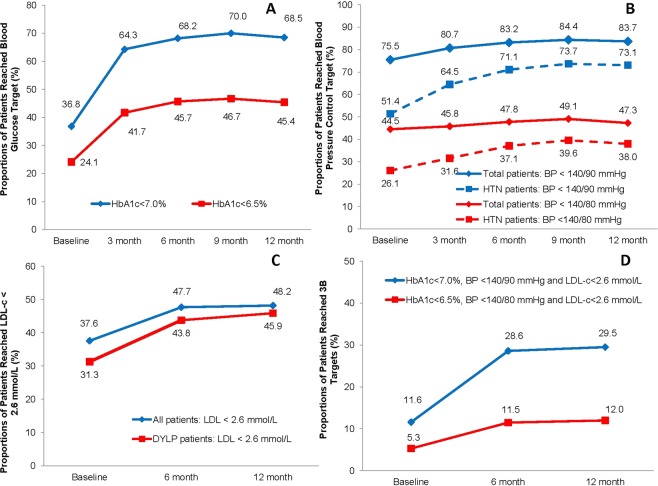
Figure 1.
Proportion of patients reaching the target of HbA1c <7.0%, BP <140/90 mmHg, LDL-C <2.6 mmol/L in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes patients at baseline and during the 12 months of follow-ups. (A) Proportion of patients reaching the target of HbA1c <7.0% at baseline and during the 12 months of follow-ups (p < 0.05), proportion of patients reaching the intensive target of HbA1c <6.5% at baseline and during the 12 months of follow-ups (p < 0.05). (B) Proportion of patients reaching the target of BP <140/90 mmHg at baseline and during the 12 months of follow-ups in total patients (p < 0.05 for trend) and in patients with hypertension (HTN) (p < 0.05 for trend), proportion of patients reaching the intensive target of BP < 140/80 mmHg at baseline and during the 12 months of follow-ups in total patients (p < 0.05 for trend) and in patients with hypertension (HTN) (p < 0.05 for trend). (C) Proportion of patients reaching the target of LDL-C <2.6 mmol/L at baseline and during the 12 months of follow-ups in total patients (p < 0.05 for trend) and in patients with dyslipidemia (DYLP) (p < 0.05 for trend). (D) Proportion of patients reaching the combined three therapeutic targets (HbA1c <7.0%, BP <140/90 mmHg and LDL-C <2.6 mmol/L) at baseline and during the 12 months of follow-ups (p < 0.05 for trend); proportion of patients reaching the combined three therapeutic targets (HbA1c <6.5%, BP <140/80 mmHg and LDL-C <2.6 mmol/L) at baseline and during the 12 months of follow-ups (p < 0.05 for trend).