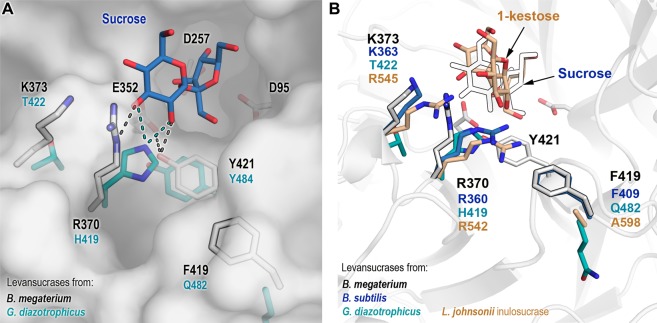
Figure 1.
Modified positions in B. megaterium levansucrase library. (A) Selected positions for mutagenesis in B. megaterium levansucrase are displayed as outlined white sticks. Catalytic amino acids and residue Y421, which has a pivotal role in hydrolysis and transfer, are shown as white sticks. Corresponding residues in the levansucrase from Gram-negative Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus are depicted in cyan. Possible hydrogen bond interactions with other residues and with sucrose are shown as dotted lines. Sucrose (blue) was aligned from the crystal structure of B. subtilis levansucrase (PDB 1pt2). (B) Residues found at analogous positions in the inulosucrase from L. johnsonii (PDB 2yft, orange) and in the levansucrases from B. megaterium (PDB 3om2, white sticks), B. subtilis (PDB 1pt2, blue) and G. diazotrophicus (PDB 1w18, cyan). Equivalent positions to Y421 are not shown in the right panel for the sake of clarity. Numbering corresponding to B. megaterium levansucrase is displayed in black, and for the other enzymes according to their color code.