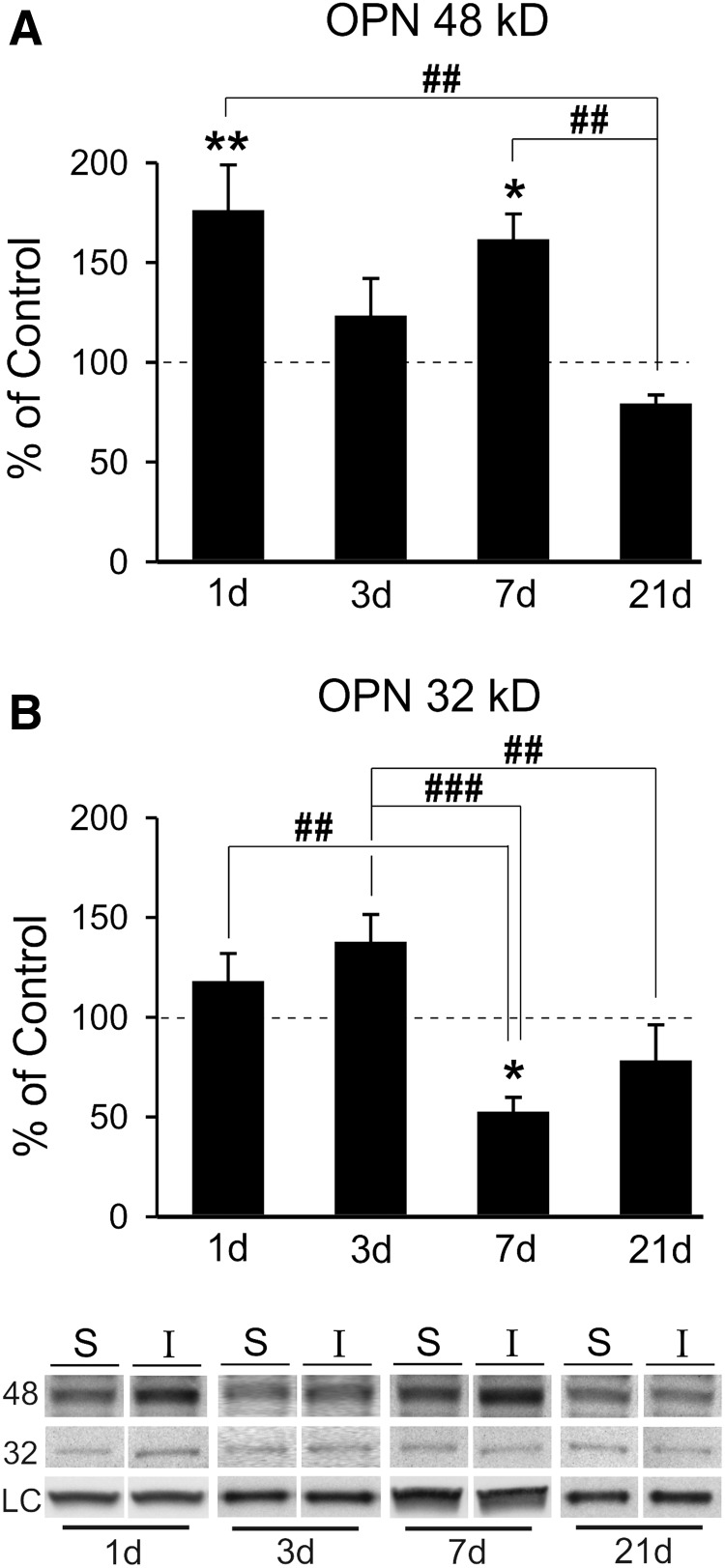
FIG. 3.
mFPI induces generation of OPN signaling fragments in the OB. (A) Post-injury analysis of 48-kD OPN showed significant elevation of the RGD signaling fragment at 1 and 7 dayd relative to sham controls. At both 3 and 21 days post-injury 48-kD OPN levels were not different from controls. Post-hoc analysis confirmed that 1- and 7-day protein signal was significantly elevated compared with that of 21 days. This pattern of 48-kD OPN correlates with peak MMP9 activity. (B) Only one post-injury change in 32-kD OPN peptide was observed, a reduction from sham controls at 7 days. Post-hoc analysis showed the 7-day reduction was significantly lower than both 1- and 3-day signal, as well as a difference between 3- and 21-day signal. Results expressed as percent of sham control ROD (100% dashed line). Representative blot images, with cyclophilin A and β-actin load controls, illustrated below. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus sham control; #p < 0.05; ##p < 0.01; ###p < 0.001; n = 4–7/group. mFPI, mild fluid percussion injury; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; OPN, osteopontin; ROD, relative optical density.