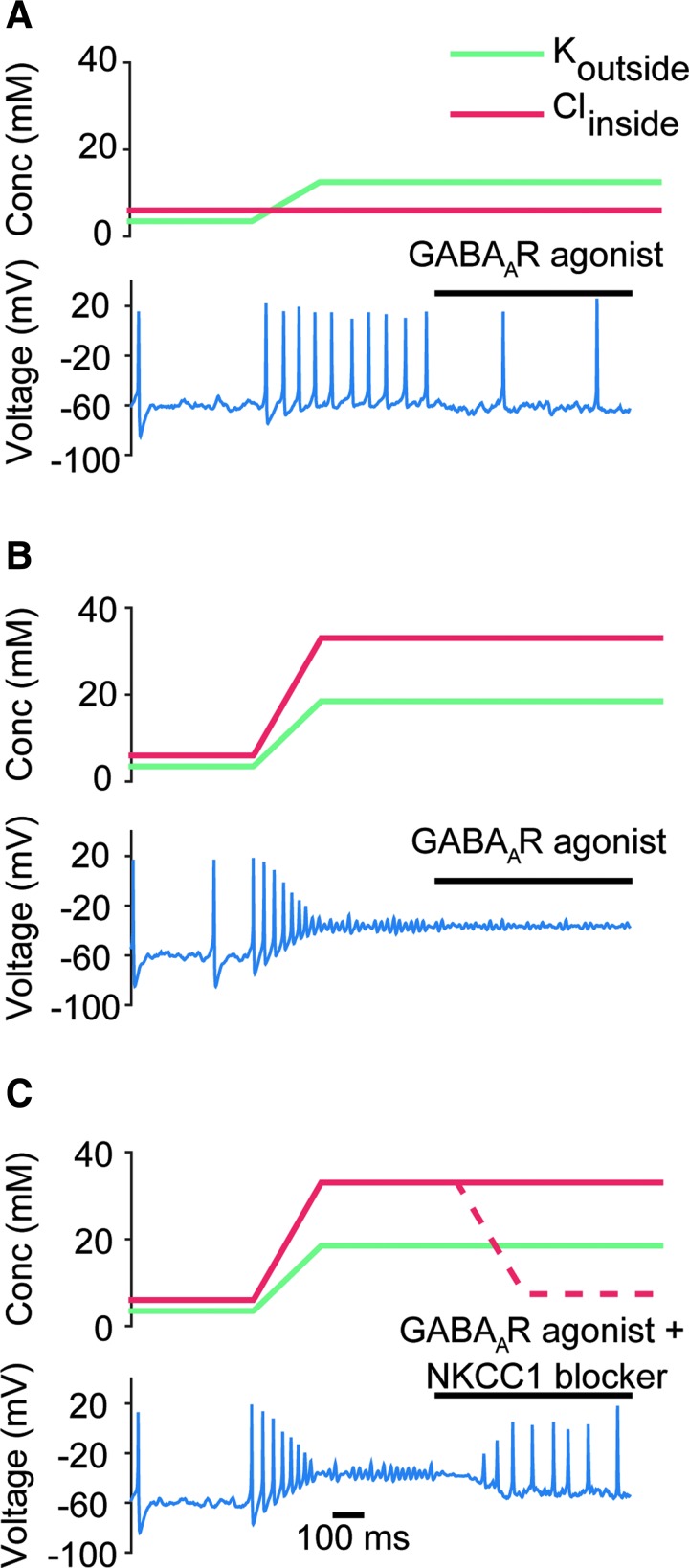
FIG. 4.
Effect of GABAA receptor agonists on the response of regular spiking (RS) neuron model in pathological brain states, in the presence and absence of Na+-K+-2Cl- (NKCC1) co-transporter blockers. (A) Response of the RS neuron model to GABAA receptor agonists in an epileptic brain state. The values of extracellular potassium and intrcellular chloride are shown in the upper panel. Under these epileptic conditions, GABAA receptor agonists can still help hyperpolarize the neuron, as would be expected from their common use as anti-epileptic drugs. (B) Same as in A, but for a post-traumatic brain injury (TBI) brain state. The GABAA agonist is unable to rescue the neuron from depolarizaiton block. (C) Response of the RS neuron model to a combination of GABAA receptor agonist and NKCC1 co-transporter blocker in a post-TBI brain state. Dotted line signifies the change in intracellular chloride caused by the effect of the NKCC1 co-transporter blocker. The combination of the two drugs is able to rescue the model neuron from depolariziation block.