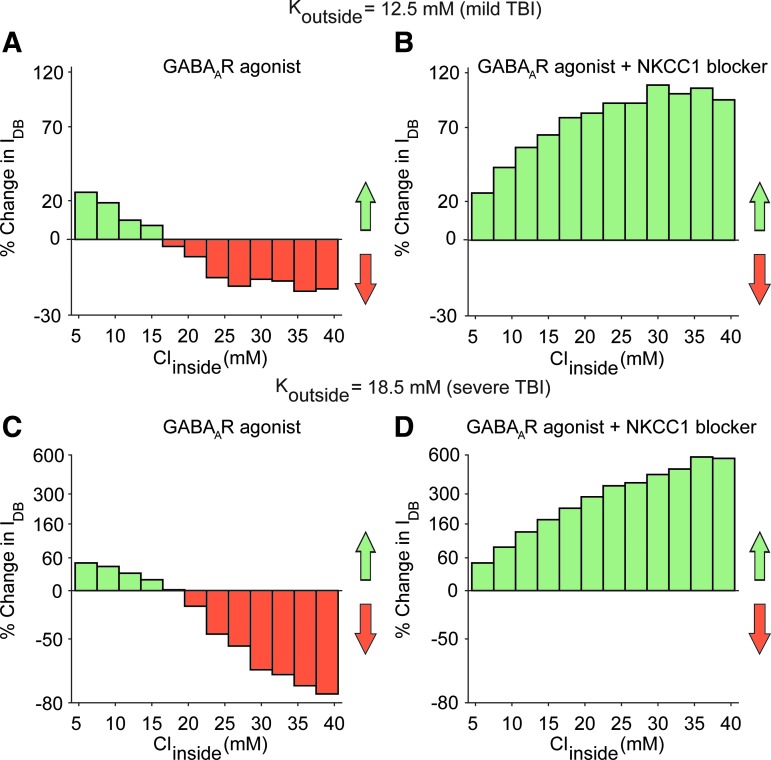
FIG. 5.
GABAA agonists, only in combination with Na+-K+-2Cl- (NKCC1) co-transporter blockers, can rescue neurons from depolariziaton block across a range of pathological ion concentations. (A) Effect of GABAA receptor agonists on the percent change in IDB of the regular spiking (RS) neuron model when Koutside = 12.5 mM, reflecting mild traumatic brain injury (TBI). Note that values >0 reflect a therapeutic effect, whereas values <0 reflect a pathological worsening. Under these potassium conditions, GABAA receptor agonists can reduce the propensity to depolarization block when intracellular chloride concentrations are close to the normal physiological range, but exert little or negative effect when chloride concentrations inside the cell exceed the physiological range. (B) Same as in A, but for the combination of a GABAA receptor agonist and NKCC1 co-transporter blocker. By blocking NKCC1 co-transporter and hence reducing intracellular chloride concentration, this combination of drugs can rescue the model neuron from depolariziation block across a wide range of intracellular chloride concentrations. This suggests that this combination of drugs can have a therapeutic benefit in post-TBI brain states. (C, D) Same as A, B, but for Koutside = 18.5 mM, reflecting more severe TBI.