Figure 1.
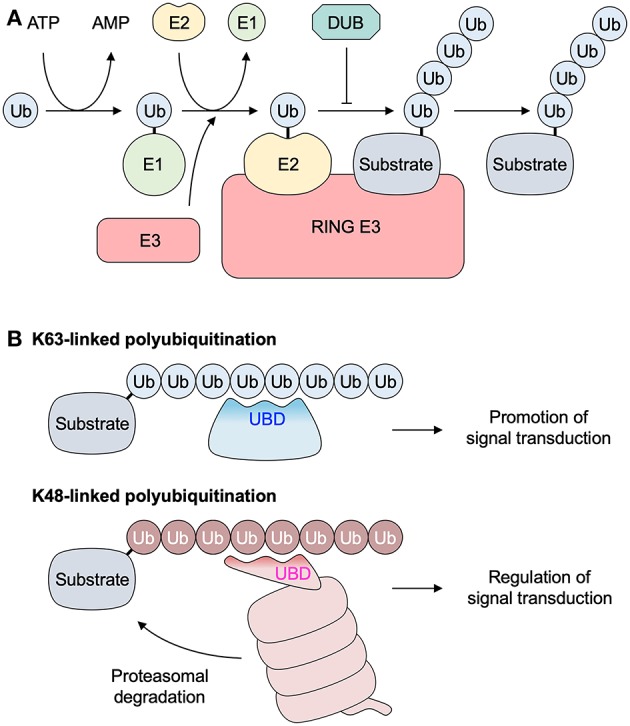
Polyubiquitination system. (A) Three enzymes catalyze the polyubiquitination of the substrate protein through a cascade of reactions: a ubiquitin-activating enzyme (E1), a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (E2), and a ubiquitin-protein ligase (E3). The E1 enzyme first forms a thiol ester bond with a ubiquitin. The activated ubiquitin is transferred to the E2. A RING E3 enzyme (such as TRAF6) functions as a scaffold for the binding of both the E2 and the target molecule, and facilitates the transfer of ubiquitin from the E2 to the target protein. (B) Lys63 (K63)-linked polyubiquitination promotes intracellular signal transduction via the association between a substrate protein with K63-linked ubiquitin chains and a protein with a UBD. K48-linked ubiquitin chains are recognized by proteasome, and subsequent proteasomal degradation of the substrate protein is involved in regulation of intracellular signal transduction in several ways. DUB, deubiquitinase; RING, really interesting new gene; Ub, ubiquitin; UBD, ubiquitin binding domain.
