Figure 3.
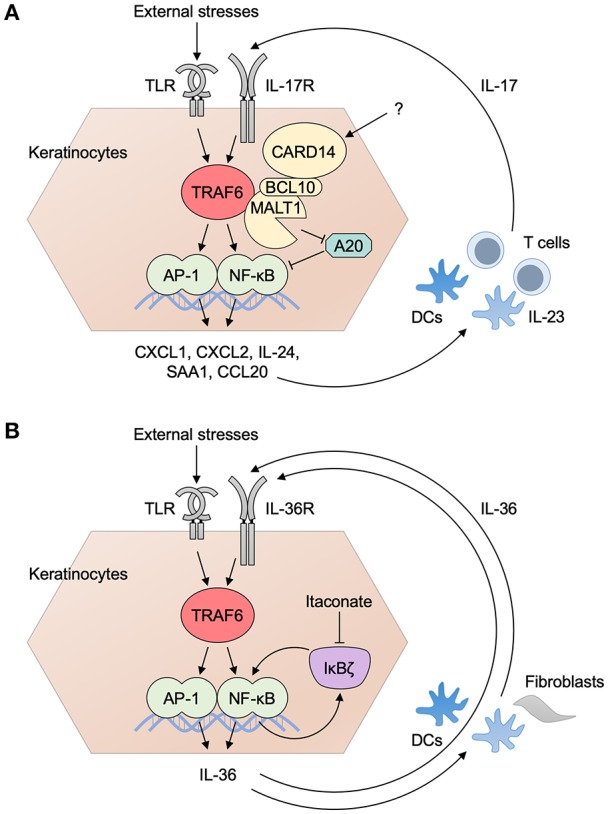
Inflammatory loops in the EIME of psoriasis. (A) The inflammatory loop of IL-17 in psoriasis. TRAF6-dependent activation of danger signals (signal 1: such as TLR pathways) induces the production of psoriasis mediator from keratinocytes. Subsequent activation of the IL-23/IL-17 axis in DC–T cell interaction gives rise to the production of IL-17 (signal 2) that drives further activation of keratinocytes. CARD14 associates with ACT1 and TRAF6 and is involved in IL-17 signaling. Activated MALT1 degrades A20 and suppresses its regulatory roles for ubiquitin signaling. (B) The inflammatory loop of IL-36 and IκBζ in psoriasis. IL-36R is an IL-1R family receptor and its signaling pathway is expected to be TRAF6-dependent. The activation of an IL-36 pathway by the ligation of IL-36 to its receptor triggers the expression of IκBζ. It promotes the transcriptional expression of itself, as well as that of a series of psoriasis mediators inducing the production of IL-17 from immune cells. IL-36 from keratinocytes binds to IL-36R in keratinocytes and other cells, such as DCs and fibroblasts, and drives the loop of IL-36 pathway. Transcriptional regulation by IκBζ is in part mediated by histone methylation. Itaconate inhibits the protein induction of IκBζ and ameliorates psoriatic inflammation. AP-1, activator protein 1; BCL10, B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 10; CARD, caspase recruitment domain-containing protein; CXCL, CXC chemokine ligand; CCL, CC chemokine ligand; DC, dendritic cell; MALT1, mucosa associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation gene 1; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; SAA, serum amyloid A; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TRAF6, tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6.
