Figure 4.
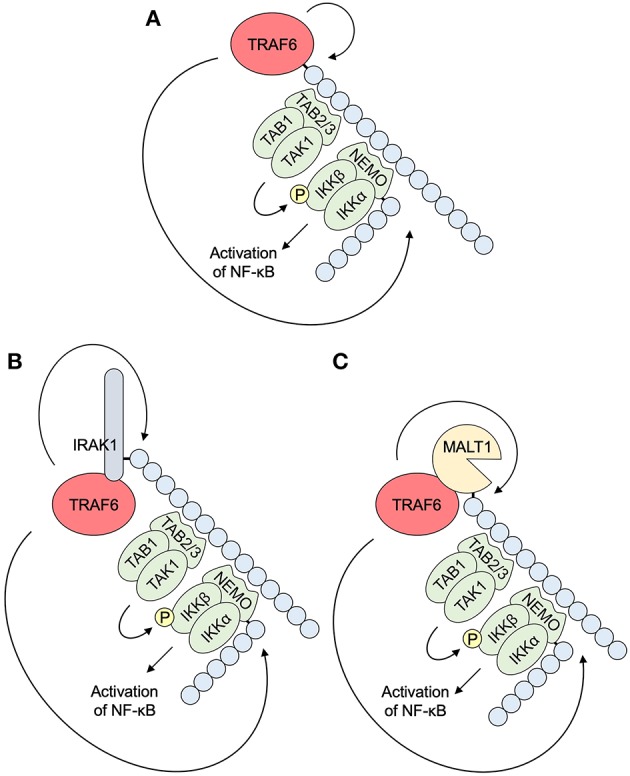
NF-κB pathways downstream of TRAF6. (A) K63-linked self-ubiquitination by E3 ligase activity of TRAF6 accumulates TAB2/3 with a UBD and triggers subsequent association and activation of TAB1 and TAK1. NEMO/IKKγ also binds to K63-linked ubiquitin chains via a UBD, and associates with IKKα and IKKβ. NEMO ubiquitination by TRAF6 promotes the formation of an IKK complex. TAK1 activation is followed by the activation of MAPK pathways. IKKβ phosphorylation by TAK1 results in the activation of NF-κB pathways. (B) TRAF6 E3 ligase activity polyubiquitinates IRAK1, an upstream molecule of TRAF6 in IL-1/TLR pathways (see A). (C) TRAF6 E3 ligase activity polyubiquitinates MALT1, a component of a signalosome in TCR/BCR pathways, CLR pathways, and others (see Figure 2D). IKK, IκB kinase; IRAK, interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase; MALT1, mucosa associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation gene 1; NEMO, NF-κB essential modulator; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; TAB, TAK1 binding protein; TAK1, transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase 1; TRAF6, tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6.
