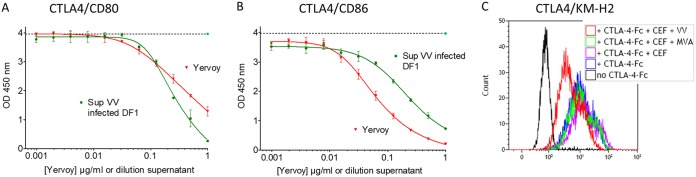
FIG 1.
Culture supernatants of vaccinia virus-infected cells inhibit the binding of hCTLA4-Fc to CD80 or CD86. DF1 cells were infected by vaccinia virus (Copenhagen TK− RR−) at an MOI of 0.05. Forty-eight hours after infection, culture supernatants were recovered, centrifuged, filtered, and tested by ELISA as follows. A total of 250 ng of hCTLA4-Fc was coated on an ELISA plate, and 2-fold serial dilutions of supernatant (Sup) or ipilimumab (Yervoy) (starting at 1 μg/ml) were added concomitantly with either 25 ng/ml of His-tagged hCD80-Fc (A) or 100 ng/ml hCD86-Fc (B) protein. The binding of B7 proteins to CTLA4 was monitored using an HRP-conjugated anti-His antibody. Each represented value is the mean (± standard deviation) of triplicate wells. The dotted lines correspond to the signals obtained with the undiluted supernatant of the uninfected cells. (C) CEFs were infected by vaccinia virus (Copenhagen TK− RR−) at an MOI of 0.05. Forty-eight hours after infection, culture supernatants were recovered, centrifuged, filtered, and tested as follows. Culture supernatants were tested for their blocking activity on the hCTLA4–Fc interaction with KM-H2 cells by flow cytometry. A total of 1 × 105 cells was first stained using Live/Dead Fixable Violet Dead Cell Stain kit and then incubated with PBS (no CTLA4–Fc) or with 100 ng/ml CTLA4–Fc in the presence or absence of culture supernatants from virus-infected or uninfected CEFs. CTLA4–Fc binding was detected with 5 μg/ml PE-conjugated anti-human IgG Fc and analyzed within the live singlet population. OD, optical density.