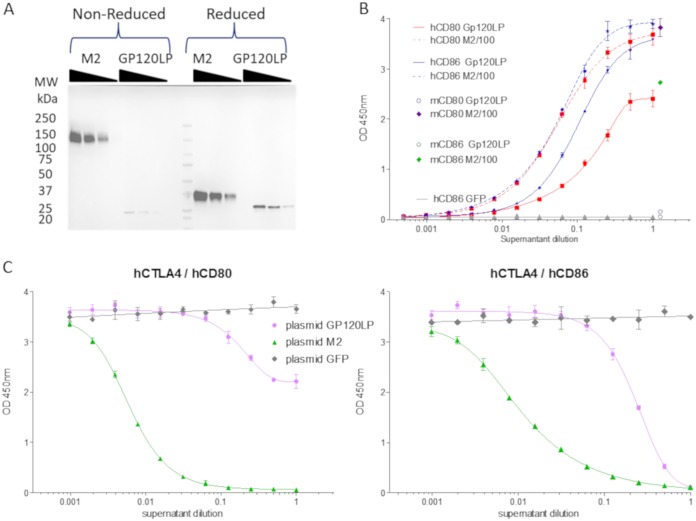
FIG 9.
The Gp120LP myxoma virus M2 homolog protein binds to human CD80 and CD86 proteins but not to their murine counterparts. (A) FLAG-tagged recombinant Gp120LP protein, a myxoma virus homolog of vaccinia virus M2, was produced in supernatant of transiently transfected HEK293 cells. Different volumes (10, 5, and 2.5 μl) of the culture supernatants of cells transfected by a plasmid encoding either M2 or Gp120LP were loaded on 4% to 15% SDS-PAGE gels and transferred on PVDF membranes. The recombinant proteins were detected using an anti-Flag-HRP antibody and an enhanced chemiluminescence kit. MW, molecular weight. (B) The same supernatants were assessed for murine and human CD80-Fc and CD86-Fc binding as described in the legend of Fig. 8B. Undiluted supernatant of cells transfected with a plasmid encoding Gp120LP or 100-fold-diluted culture supernatant of cells transfected with a plasmid encoding M2 was added to plates coated (at 1 μg/ml) with human and murine CD80-Fc and CD86-Fc. Samples were then diluted (2-fold serial dilution) in blocking solution, and bound recombinant protein was detected by an HRP-conjugated anti-Flag antibody. Each represented value is the mean (± standard deviation) of triplicate wells. The binding levels to human B7 proteins are represented as full curves with either dashed lines (supernatant of cells transfected with a plasmid encoding M2 diluted 100-fold as starting material) or plain lines (supernatants of cells transfected with a plasmid encoding Gp120LP or GFP). For the sake of clarity, only the first points are presented for the binding to murine B7 proteins of the 100-fold-diluted supernatant of cells transfected with a plasmid encoding M2. (C) Supernatants were also tested for their ability to inhibit the hCTLA4-hCD80/hCD86 interaction in the same assay as described in the legend of Fig. 1 Supernatant of untransfected cells or cells transfected with a plasmid encoding GFP were used as negative controls. Each represented value is the mean (± standard deviation) of triplicate wells.