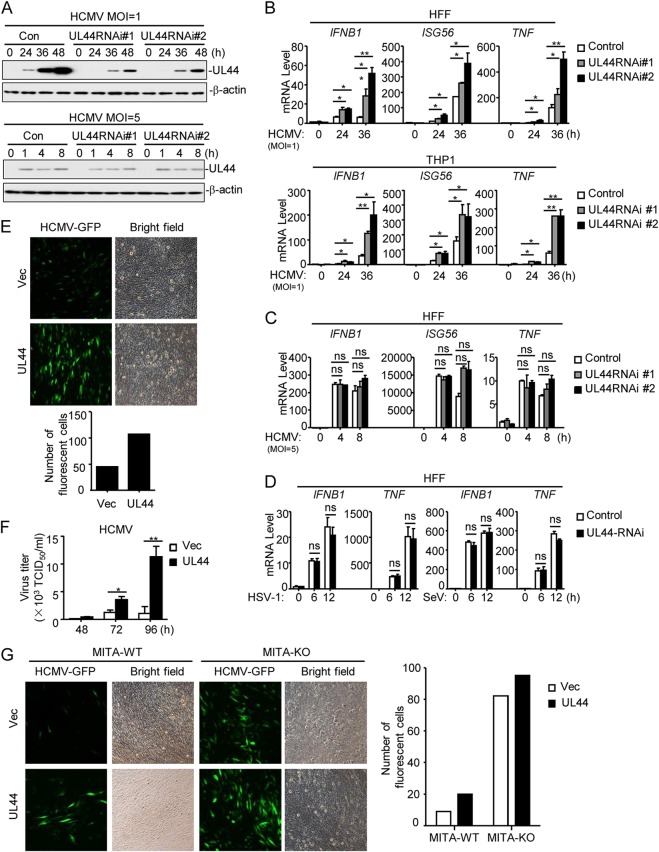
FIG 2.
UL44 deficiency increases HCMV-induced expression of downstream antiviral genes. (A) Effects of UL44-RNAi on the expression of HCMV UL44. HFFs stably expressing UL44-RNAi (2 × 106) were infected with HCMV (MOI, 1 or 5) for the indicated times before immunoblot analyses were performed. (B) Effects of UL44-RNAi plasmids on HCMV-induced transcription of antiviral genes. HFFs or THP1 cells stably expressing UL44-RNAi (5 × 105) were infected with HCMV (MOI, 1) for the indicated times before qPCR analysis. (C) Effects of UL44-RNAi on HCMV-induced transcription of antiviral genes. HFFs stably expressing UL44-RNAi (5 × 105) were infected with HCMV (MOI, 5) for the indicated times before qPCR analysis. (D) Effects of UL44-RNAi plasmids on HSV-1- or SeV-induced transcription of antiviral genes. HFFs stably expressing UL44-RNAi (5 × 105) were infected with HSV-1 or SeV (each at an MOI of 1) for the indicated times before qPCR analysis. (E) UL44 promotes HCMV production. Control HFFs or HFFs stably expressing UL44 (2 × 105) were infected with HCMV-GFP (MOI, 1), and the supernatants were harvested at 96 h postinfection before fluorescence microscopy. (F) UL44 enhances virus replication. Control HFFs or HFFs stably expressing UL44 (2 × 105) were infected with HCMV (MOI, 1), and the supernatants were harvested at the indicated times postinfection for measurement of viral titers by standard TCID50 assays. (G) UL44 enhances HCMV replication by inhibiting cellular antiviral responses in HFFs. MITA-deficient (knockout [KO]) HFFs were generated with CRISPR-Cas9 technology. MITA-KO and control (wild-type [WT]) HFFs (2 × 105) were infected with HCMV-GFP (MOI, 1), and the supernatants were harvested at 96 h postinfection before florescent microscopy. Graphs show means ± SD (n = 3). Asterisks indicate significant differences (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01) by the unpaired t test; ns, not significant.