Fig. 7.
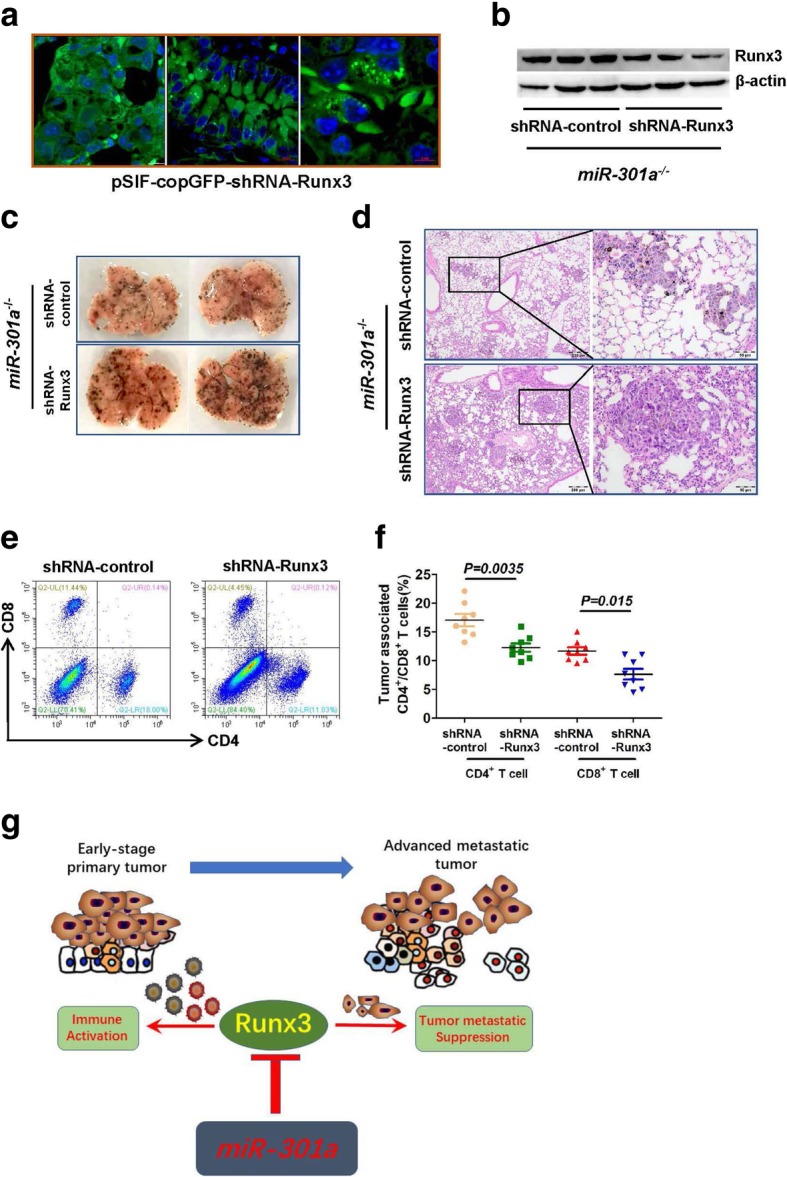
Inhibition of tumor metastasis in miR-301a−/− mice correlates with elevated Runx3 expression and CD8+ T cell infiltration. miR-301a−/− mice (n = 8 per group) were implanted with B16 tumor cells by intravenous injection. After 48 h, shRNA control or shRNA-Runx3 lentivirus was injected into miR-301a−/− mice every day until mice were sacrificed and lung tissues collected. (a) Expression of GFP from the shRNA-Runx3 vector in B16 lung tumors. Scale bars = 10 μm or 5 μm. (b) Runx3 expression in lung sections from miR-301a−/− mice (n = 3) with either shRNA-control or shRNA-Runx3 as determined by western blot. (c) Images of representative B16 tumors in the lung from miR-301a−/− mice with either shRNA-control or shRNA-Runx3 lentivirus (n = 8 per group). (d) H&E-stained sections of lungs isolated from miR-301a−/− mice (n = 8 per group) with B16 tumor cells. (e) Infiltrating T cells within lung tumors. Right panel: Percentages of infiltrating CD8+ and CD4+ T cells isolated from B16 tumors implanted in miR-301a−/− mice with either shRNA-control or shRNA-Runx3 lentivirus as analyzed by flow cytometry (pregated on CD3 events). Left panel: CD4+ and CD8+ T cells counts in lung sections (n = 8 per group). (f) Schematic representation of the roles of miR-301a and Runx3 in lung tumorigenesis. Values represented the mean ± s.d. of three independent experiments. **P < 0.01 or *P < 0.05 indicates a significant difference between the indicated groups (two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test in f)
