Figure 2. RhoE negatively regulates NF-κB activation in vivo and in vitro.
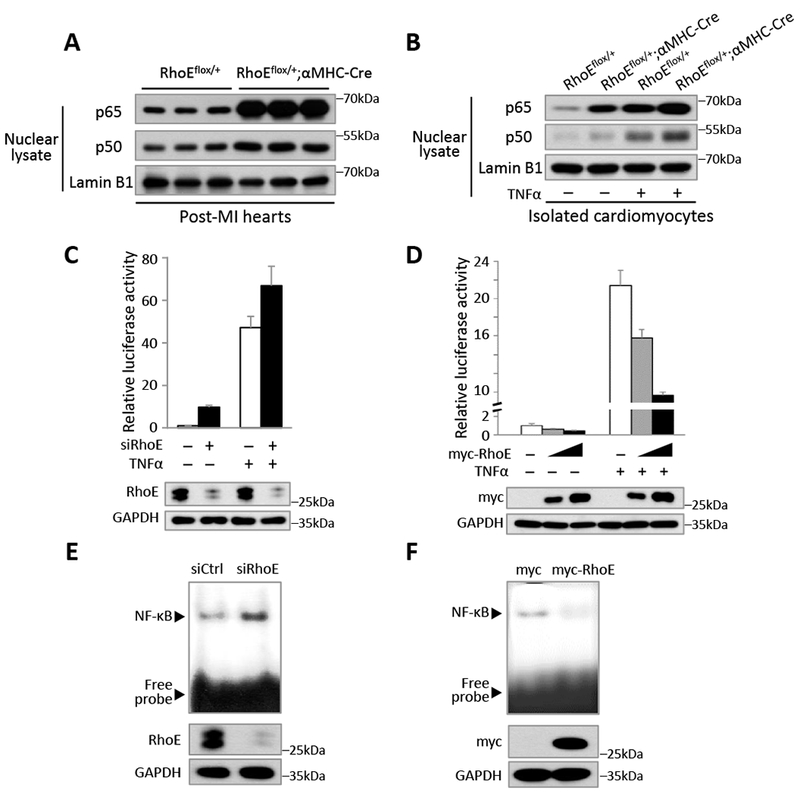
(A) Immunoblot for nuclear p65 and p50 in RhoEflox/+ and RhoEflox/+;αMHC-Cre mouse hearts on day 3 post MI. (B) Immunoblot for nuclear p65 and p50 in isolated cardiomyocytes. The cells were either untreated or stimulated with 40 ng/ml of TNFα for 15 minutes. (C-D) NF-κB-dependent reporter luciferase assay in C2C12 cells transfected with control siRNA or RhoE-specific siRNA (C), and in C2C12 cells transfected with empty vector or myc-RhoE expression construct (D). The cells were either untreated or stimulated with 40 ng/ml of TNFα for 4 hours. RhoE expression levels were assessed by immunoblot. (E-F) EMSA assay for NF-κB activity in C2C12 cells transfected with control siRNA or siRhoE (E), or in C2C12 cells transfected with empty vector or myc-RhoE expression construct (F).
