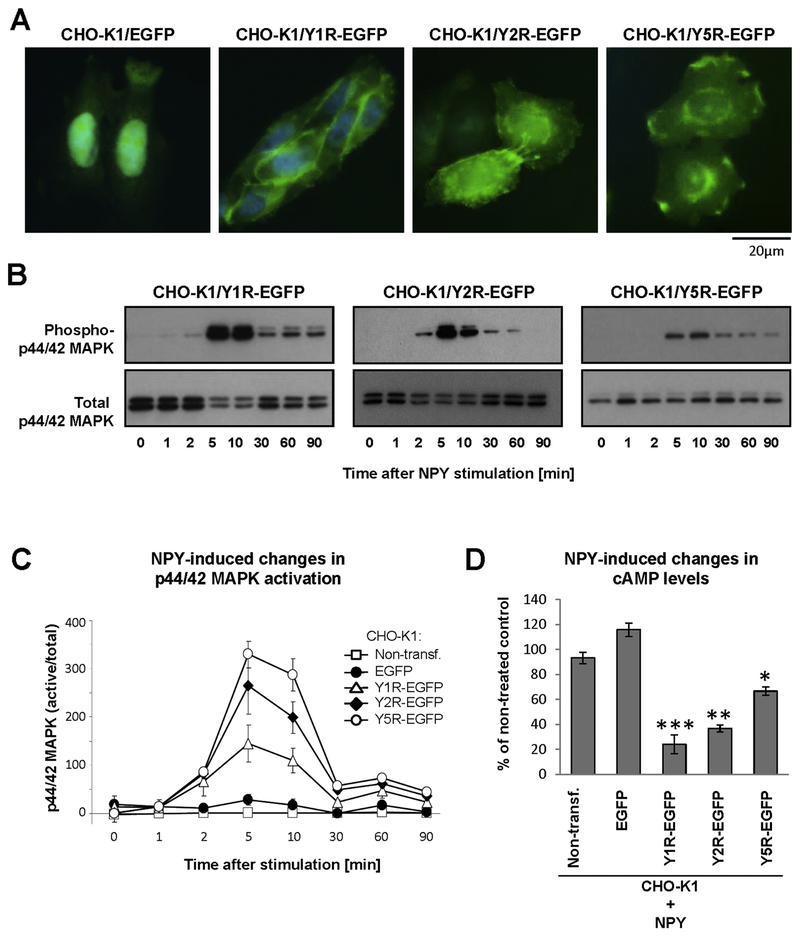
Figure 1. NPY receptors fused to fluorescent proteins preserve their functions.
A. Microscopic images of CHO-K1 cells stably transfected with EGFP alone or NPY receptors fused to EGFP. B. p44/42 MAPK activation induced by NPY in CHO-K1 cells stably transfected with its receptors fused to EGFP. The cells were treated with NPY at a concentration of 10−7M, and phosphorylated and total p44/42 MAPK were detected by Western blot. C. Densitometric quantification of p44/42 MAPK activation in NPY-treated CHO-K1 cells stably transfected with NPY receptor-EGFP fusion proteins. D. NPY-induced changes in cAMP levels in CHO-K1 cells expressing NPY receptors fused to EGFP. The cells were treated with forskolin in the presence or absence of NPY at a concentration of 10−7M for 1h, and the cAMP levels were measured by enzyme immunoassay. The graph represents an average of three independent experiments, 2 wells per treatment each. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01 and ***p<0.001 vs. NPY-treated nontransfected control by t-test.