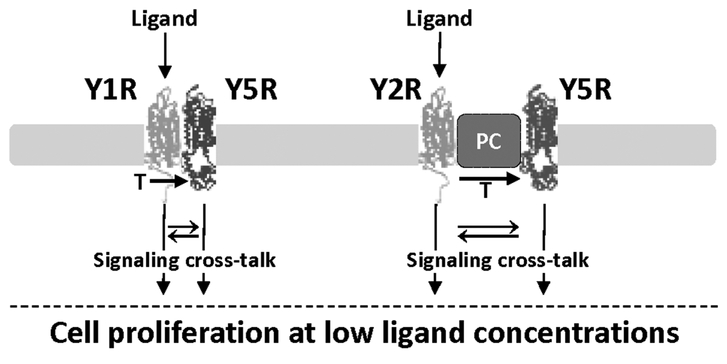
Figure 9. Model of the mechanisms underlying increased ligand sensitivity in cells expressing heterotypic NPY receptors.
Y1R and Y5R form heterodimers, while Y2R and Y5R are not directly bound, yet interact with each other, possibly as a part of the larger protein complex (PC). However, in either case, activation of one receptor in the complex leads to transactivation (T) of the other NPY receptor and signaling from both receptors. This, in turn, may trigger signaling cross-talk between pathways activated by these receptors and thereby enhance their functional effects. Consequently, cells expressing heterotypic NPY receptors proliferate in response to low ligand concentrations.