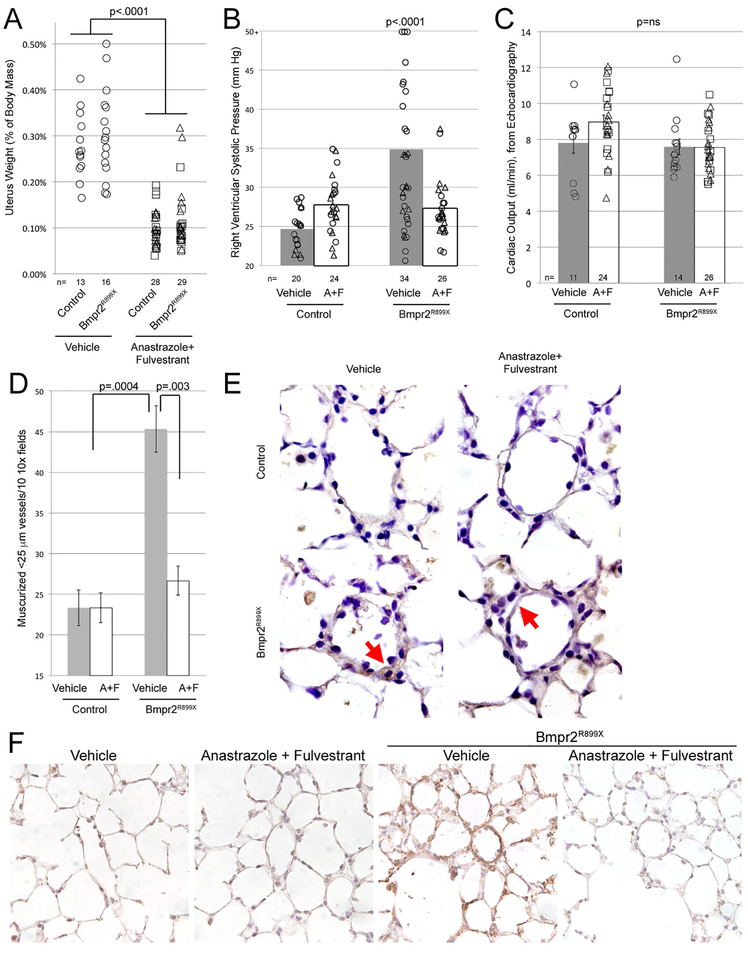
Figure 1 –
(A) Anastrozole & Fulvestrant (A+F) reduce uterine weights in mice (p<0.0001) as expected; by multiple ANOVA, R899X mutation did not have an effect on uterine weights. Each symbol is the measurement from one mouse. (B) Anastrozole & Fulvestrant delivered in osmotic pumps through the final four weeks of six weeks’ BMPR2R899X transgene induction prevents development of elevated RVSP (p<0.0001 by multiple ANOVA, using transgene and drug as variables). Each symbol is a value from one mouse; symbols that are triangles also received the androgen MPA, which did not impact RVSP and so have been not been separated. Numbers of mice in each group are listed at the bottom of the plot; mice were age-matched, and controls were done contemporaneously for each group. (C) Cardiac outputs were not significantly changed by either Anastrozole & Fulvestrant treatment or Bmpr2 mutation. (D) Anastrozole & Fulvestrant nearly normalized the increase in muscularized vessels normally seen in BMPR2R899X mice. By multiple ANOVA considering BMPR2 mutation and treatment as factors, BMPR2 mutation increases muscularized vessels (p=0.0004) while A+F decrease them, specifically in BMPR2 mutant mice (p=0.003). (E) Staining for oxidized lipids demonstrates increased oxidative stress in BMPR2R899X mice, normalized with Anastrozole & Fulvestrant. (F) Ceramide (toxic lipid) staining (brown) is increased in lungs from BMPR2R899X mice, and reduced by Anastrozole and Fulvestrant.