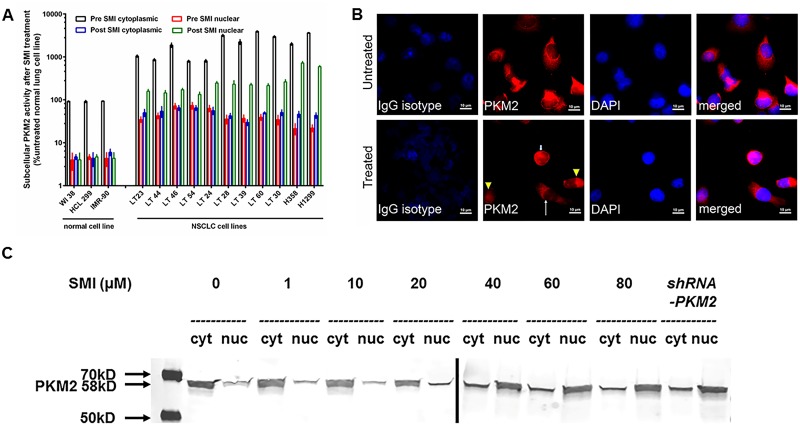
Fig 4. Effect of PKM2 inhibitor on subcellular localization of PKM2 enzymatic activities and protein levels.
(A) Three normal lung and 11 NSCLC cell lines were incubated with 65 μM of PKM2 inhibitor for 48 hours. Cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions were separated for PKM2 enzyme activity determination. Each value is expressed as mean % cytoplasmic activity in untreated normal lung cell lines. (B) 25,000 H358 cells were plated in a multiwell-glass chamber and incubated for 48 hours with or without 65 μM of PKM2 inhibitor. Then, IFA was performed. PKM2 was stained with Alexa 594 (red). Untreated cells stained with anti-PKM2 antibody showed spindle-shaped morphology with red cytoplasm and hollow nucleus while treated cells showed various patterns of red signals; low signal in both cytoplasm and nucleus (arrow head), small cells with intense signal in both cytoplasm and nucleus (small arrow), and spindle-shaped cells with red cytoplasm and hollow nucleus (big arrow). (C) Western blot analysis for PKM2 was performed from cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of a NSCLC cell line treated with 10–80 μM of SMI or shRNA-PKM2.