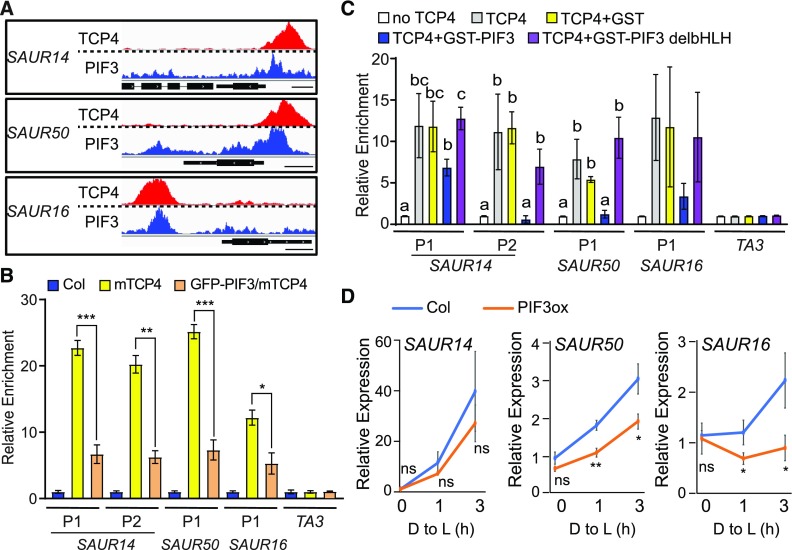
Figure 6.
PIF3 Inhibits the Binding of TCP4 to the Promoters of SAUR Genes and Represses Their Expression.
(A) The binding area of PIF3 overlaps with that of TCP4 at the SAUR promoter regions. The raw reads of PIF3 ChIP-seq (Zhang et al., 2013) and TCP4 ChIP-seq (this study) at the SAUR14, SAUR50, and SAUR16 loci are shown. Bars = 250 bp.
(B) PIF3 overexpression inhibits the binding of TCP4 to the SAUR promoters in the dark. Four-day-old dark-grown seedlings of the indicated genotype were used for ChIP assays. Relative enrichment value in Col was set to 1. TA3 was used as an internal control. Data are shown as the mean ± se of three biological replicates. Statistical analysis was performed by two-tailed Student’s t test: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.
(C) PIF3 inhibits the binding of TCP4 to the SAUR promoters in vitro, and this inhibition requires the PIF3 DNA binding domain. In vitro–translated TCP4-Myc proteins captured on anti-Myc agarose were incubated with fragmented genomic DNA in the presence or absence of recombinant GST, GST-PIF3, or GST-PIF3 without the bHLH domain (GST-PIF3 delbHLH). Bound DNA was analyzed by qPCR. Data are shown as the mean ± se of three biological replicates. Different letters represent significant differences (P < 0.05 by one-way analysis of variance).
(D) Four-day-old dark-grown (D) Col and 35S:PIF3-Myc (PIF3ox) seedlings were transferred to the light for 1 or 3 h, and RNA from cotyledon tissues was analyzed to measure the expression of the indicated SAUR genes. Data are the mean ± sd of three biological replicates. Statistical analysis was performed by two-tailed Student’s t test: ns, P > 0.05; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. D to L: dark to light; PIF3ox, 35S:PIF3-Myc seedlings.