Figure 7. Genomic and non-genomic estrogen signaling pathways.
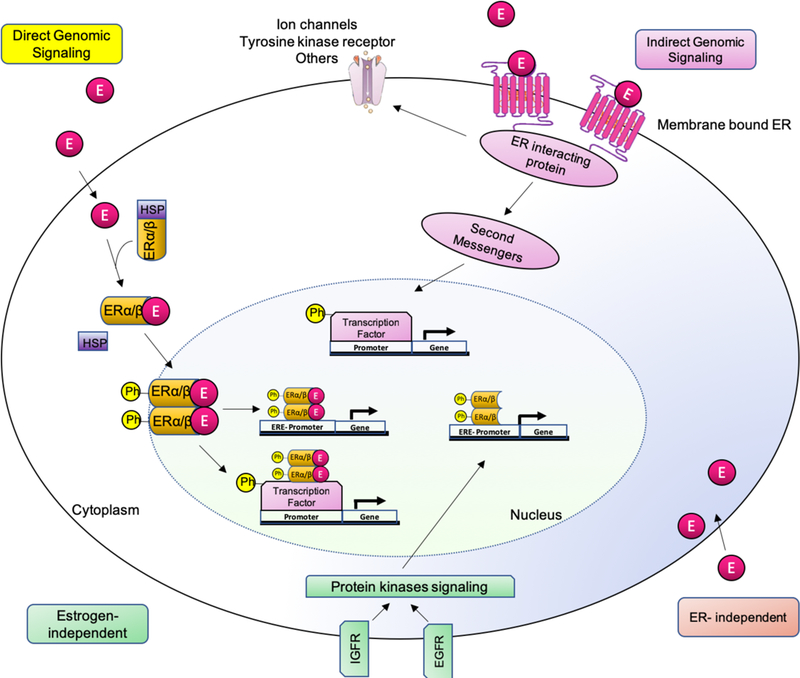
There are different estrogen-mediated signaling mechanisms. 1) Direct genomic signaling: estrogen binds to ERs. The complex dimerizes and translocate to the nucleus inducing transcriptional changes in estrogen-responsive genes with or without EREs. 2) Indirect genomic signaling: the membrane bound receptor induces cytoplasmic events such as modulation of membrane-based ion channels, second-messenger cascades and transcription factors. 3) ER-independent: estrogen exerts antioxidant effects in an ER-independent manner. 4) Estrogen independent: ligand-independent genomic events.
