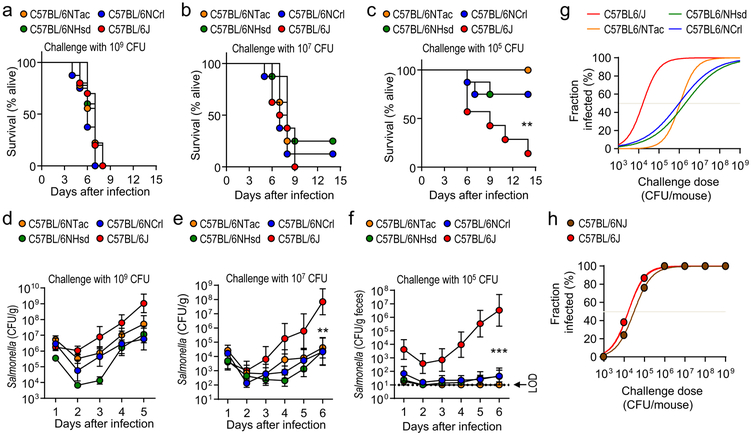
Figure 1: Phenotypic variation in the susceptibility to Salmonella infection is observed in C57BL/6 mice from different vendors.
(a-g) Mice from Charles River Laboratories (C57BL/6NCrl), Harlan (C57BL/6NHsd), Taconic Farms (C57BL/6NTac) or Jackson Laboratories (C57BL/6J) were challenged with S. Typhimurium (n = ≥7). Lethal morbidity (a-c) and S. Typhimurium shedding with the feces (d-f) were monitored at the indicated time points after challenge with 109 CFU (a and d), 107 CFU (b and e) or 105 CFU (c and f) per animal. (g) Fraction of animals developing intestinal carriage at different S. Typhimurium challenge doses. (d-f) Dots represent geometric means ± standard error of the mean. (h) Two C57BL/6 substrains (C57BL/6J and C57BL/6NJ) from Jackson Laboratories were challenged with different S. Typhimurium doses and the fraction of animals developing intestinal carriage determined (n = 3–8 per dose). LOD, limit of detection; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001.