Fig 6. Post-treatment of PAME (0.02 mg/Kg, IP) immediately after ACA enhanced functional learning/memory.
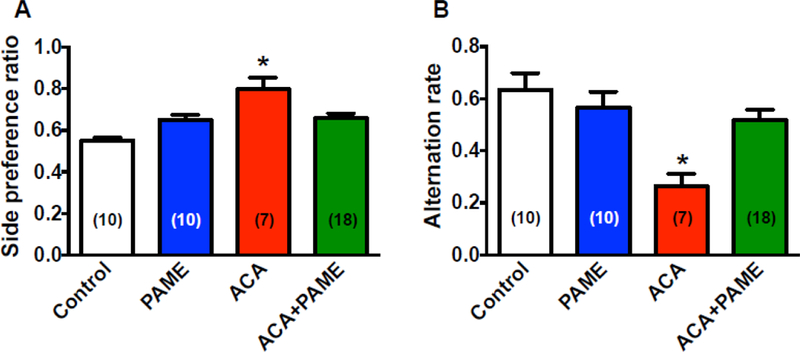
We utilized the modified spontaneous alternation protocol to detect possible hippocampal lesions associated with ACA [26, 59]. (A) A significant increase in side-preference ratio was observed in rats treated with ACA, which suggests that rats with hippocampal injury developed a side-preference[26]. Post-treatment of PAME (ACA+PAME, 0.02 mg/kg, IP) alleviated ACA-induced side-preference ratio suggesting that PAME can reduce hippocampal injury after ACA. Spontaneous alternation ratio was decreased in ACA-treated rats as compared to normal control and PAME only-treated rats, while post-treatment of PAME (ACA+PAME) at 0.02 mg/kg enhanced spontaneous alternation rate after ACA indicating that PAME can alleviate ACA-induced short-term memory deficits. Results were expressed as mean ± SEM. *p≤0.05 indicates significantly different from all groups, evaluated by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test. n indicates number of experiments.
