Figure 4.
Antigenic Profile of the MT145K Trimer
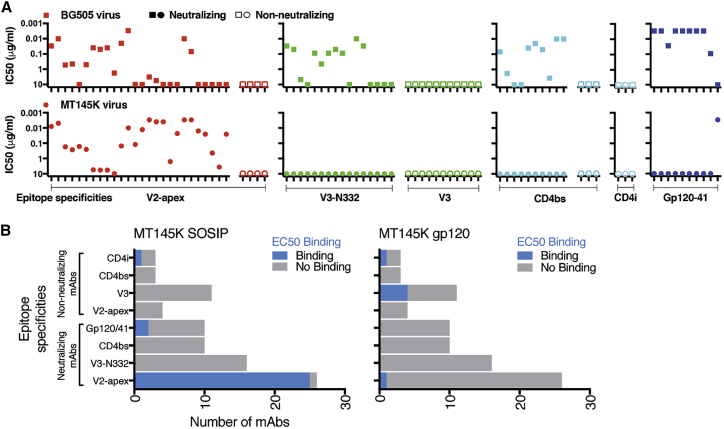
(A) HIV Env-specific mAbs were used to characterize the antigenicity of the MT145K Env trimer. MAbs targeting neutralizing and non-neutralizing epitope specificities, including V2-apex, V3-N332, linear V3, CD4bs, CD4i, and the gp120-41 interface were tested with MT145K and BG505 Env-encoding pseudoviruses in a TZM-bl cell-based reporter assay. The reciprocal IC50 neutralization titers for each virus are indicated as dot plots; plots for individual epitope specificities are depicted separately. The neutralization sensitivity comparison of BG505 and MT145K viruses against the mAb panel shows a selectively potent neutralization of MT145K by V2-apex bnAbs but no other bnAbs, except a single gp120-gp41 interface bnAb, 35022. The BG505 virus was neutralized by bnAbs targeting diverse Env sites.
(B) The above mAb panel was further tested with PGT145 Ab-purified MT145K trimer and Galanthus nivalis lectin (GNL)-purified MT145K gp120 monomer by ELISA. The binding, represented as EC50 binding titers, shows selective binding of MT145K by V2-apex bnAbs. Two of the gp120-gp41 interface bnAbs and a CD4i mAb also showed significant binding to the MT145K trimer. Four of the non-neutralizing mAbs specific to a linear V3 epitope exhibited binding to MT145K gp120, but not to the trimer.