Figure 5.
A Close-Up View of Regions on the MT145K Trimer That Correspond to Those Recognized by HIV bnAbs on HIV Trimers
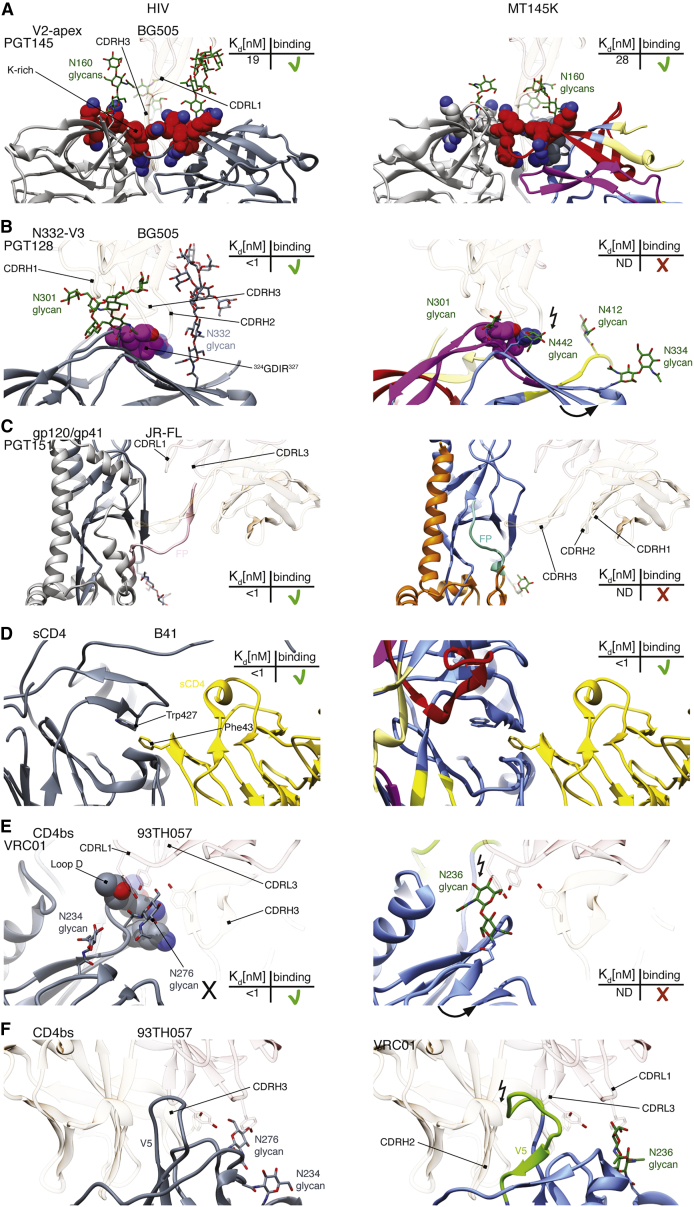
(A) V2-apex bnAb binding region: cryo-EM model of PGT145 bnAb (HC, transparent sandy brown; LC, transparent orchid) in complex with the BG505 SOSIP trimer depicting V1V2 loops in ribbon representation (Lee et al., 2017; PDB: 5V8L). The strand C K-rich region (166RDKKQK171; red spheres) and the glycan N160 (forest green sticks) that form the epitope for PGT145 bnAb are indicated. The elements in the core epitope interact with the CDRL1 loop and the long CDRH3 loop that penetrates through glycans to reach the positively charged surface underneath. Both glycan N160 and the positively charged protein residues are conserved between BG505 HIV and MT145K SIV Env trimers.
(B) V3-glycan bnAb binding region: cryo-EM model of PGT128 bnAb (HC, transparent sandy brown; LC, transparent orchid) in complex with the BG505 SOSIP trimer (Lee et al., 2015; PDB: 5ACO). The V3 loop protein backbone residues (324GDIR327; depicted in purple spheres) and the glycans N301 and N332 form the bnAb epitope and are shown to interact with the antibody CDR loops. The MT145K trimer has a glycan at N334 rather than N332 and the glycan points away from the expected location of the PGT128 Ab paratope. In addition, MT145K Env has glycans at two positions, N412 (positioned differently on HIV Env) and N442 (absent on HIV Envs), and particularly the latter will clash with PGT128 CDRH2 and prevent it from interacting with the protein part of the epitope.
(C) The gp120-gp41 interface bnAb binding region: cryo-EM model of PGT151 bnAb bound to a membrane-extracted clade B JRFL Env trimer. The structure depicts PGT151 bnAb CDRs interacting with gp120 and the gp41 interface regions (Lee et al., 2016; PDB: 5FUU). PGT151 CDRH3 interacts with the epitope formed by the protein backbone (in both gp120 and gp41), including the fusion peptide (depicted in pink) and the gp120 (N88, N448) and gp41 (N611 and N637) glycans (not shown). PGT151 Ab CDR loops interact with the FP region on the BG505 trimer. The MT145K trimer FP region (cyan) remains hidden inside the trimer.
(D) Cryo-EM model of two-domain human sCD4 with the B41 SOSIP trimer (Ozorowski et al., 2017; PDB: 5VN3). The structure shows how the Phe43 residue on sCD4 stacks into the Env cavity lining Trp427. This Trp427 cavity is conserved between HIV and MT145K Envs to accommodate CD4 binding.
(E and F) The CD4bs bnAb binding region: crystal structure of VRC01 bnAb in complex with 93TH057 gp120 (Zhou et al., 2010; PDB: 3NGB). The structure depicts VRC01 CDRH3, CDRL3, and CDRL1 loops interacting with the protein residues in loop D (HXB2: 278-282) and the glycan at N276 (E and F, left panels). The MT145K trimer lacks the N276 glycan and bears glycan N236 (unique to SIV Env) in place of N234 that would clash with the VRC01 CDRL1 loop (E and F, right panels). Additionally, the MT145K Env trimer has a longer gp120-V5 loop due to a six-amino-acid insertion at HIV HXB2-456 residue that would shift the loop such that it clashes with the CDRH2 the VRC01 Ab.