Fig. 5.
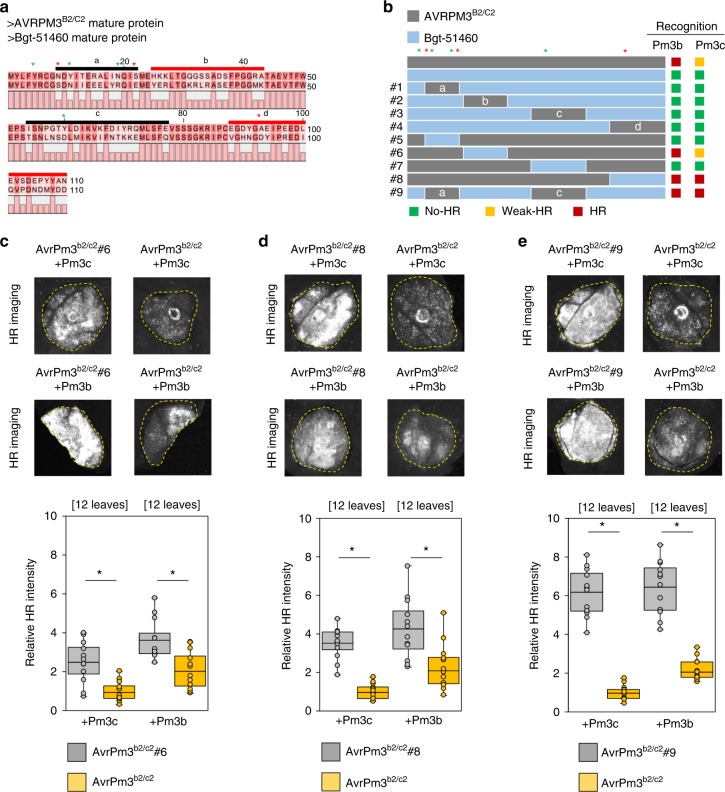
Consequence of synthetic domain swaps on the recognition of AVRPM3B2/C2. a–b Consequence of synthetic domain swaps on the AVRPM3B2/C2 AVR function. a Protein sequence alignment of the mature protein of AVRPM3B2/C2-A and the closest family member Bgt-51460. Swapped domains are indicated and labelled a, b, c and d. Domains that do not abolish AVR recognition when introduced from Bgt-51460 into AVRPM3B2/C2 are indicated in red. b Schematic representation of the protein domains swapped between AVRPM3B2/C2 (grey) and Bgt-51460 (blue). a, b Position of the residues identified from the natural sequence diversity (Fig. 4b, d) are indicated with asterisks. The impact of individual residues on AVR recognition is indicated with green for mutations with a disruptive effect, and red for mutations, with a neutral effect, according to the results summarised in Fig. 4b, d. c–e Transient expression assays in N. benthamiana indicating recognition (upper panel) and HR quantification (lower panel) for AVRPM3B2/C2 swaps #6 (c), swap #8 (d) and swap #9 (e) by Pm3c, and Pm3b. The number or independent leaf replicates is indicated. Mean values are indicated by the middle line in the boxplot. Individual data points are plotted along the whiskers delineating minimum and maximum values. Statistical significance was assessed with a two-sided Student’s t-test for paired data and indicated with (*p < 0.05). Complete N. benthamiana leaf pictures and raw data underlying the reported averages are provided in a Source Data File