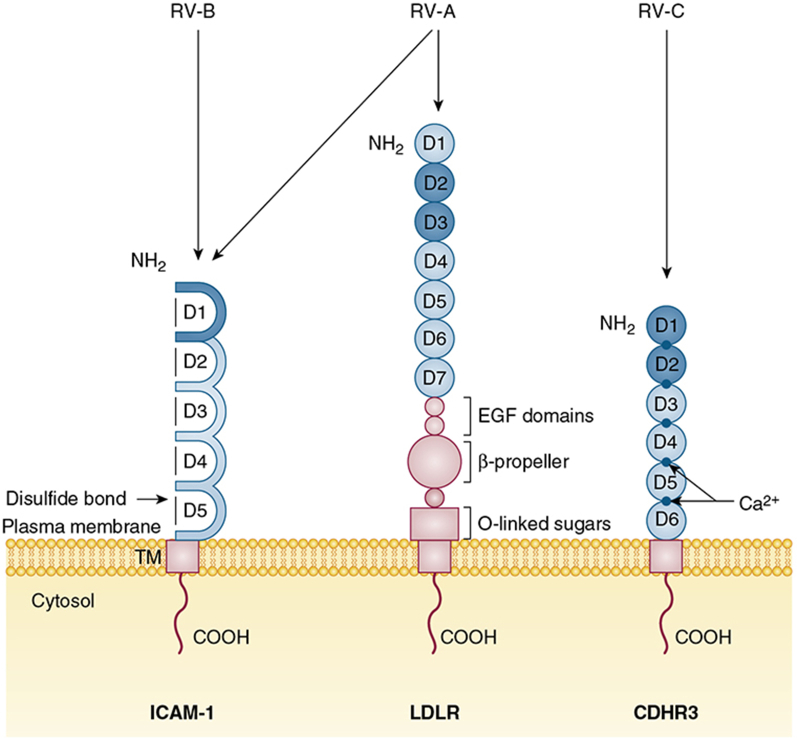
Figure 2.
Cellular receptors of RV-A, RV-B, and RV-C. ICAM-1 has five consecutive extracellular ligand binding immunoglobulin domains linked by disulfide bonds. The NH2 domain (D1) interacts with major group RV-A and all RV-B. The LDLR family of glycoproteins (receptors LDLR, VLDLR, and LDLR-related protein) are characterized by distinct repeats of ligand binding domains, EGF domains, and β-propeller modules. The LDLR receptor has seven consecutive extracellular ligand-binding domains followed by three EGF domains, a β-propeller module, and O-linked sugar domain. The NH2 second and third domains (D2 and D3) interact with minor group RV-A. CDHR3 has six extracellular ligand-binding domains structurally supported by obligate Ca2+ ions at the domain junctions. The first two NH2 domains (D1 and D2) are predicted to interact with RV-C. All RV receptors have a TM and COOH. Their virus contact domains are shaded. CDHR3 = cadherin-related family member 3; COOH = C-terminal cytoplasmic tail; EGF = epidermal growth factor; ICAM-1 = intercellular adhesion molecule 1; LDLR = low-density lipoprotein receptor; NH2 = N-terminal; TM = transmembrane region. See Figure 1 legend for expansion of other abbreviation.