Figure 2.
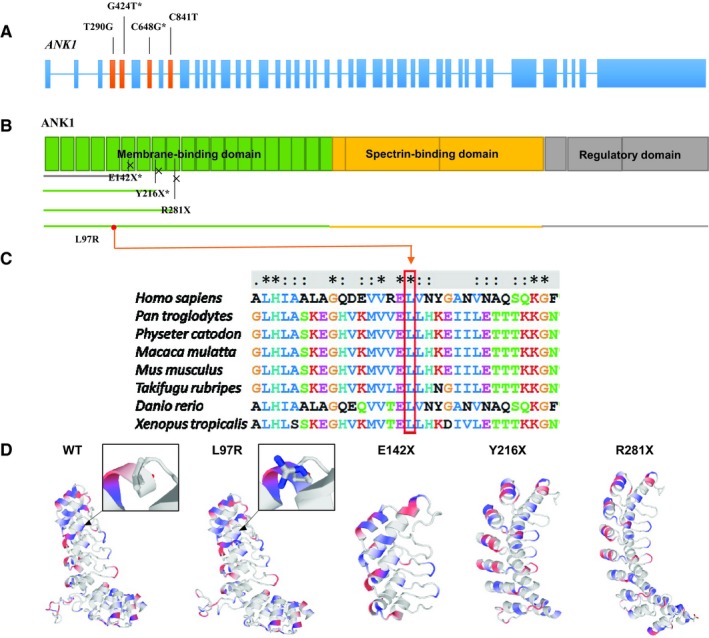
The pathogenicity of four ANK1 mutations predicted by bioinformatic analysis. (A) The structure of the ANK1 gene. The whole gene has 43 exons. Four mutations (c.T290G, c.G424T, c.C648G, c.C841T) identified in the ANK1 gene are in exons 4, 5, 7 and 9 respectively. (B) The ANK1 protein. Four mutations all occur in the membrane‐binding domain. Crosses indicate the truncation point caused by the three nonsense mutations. All the truncated proteins lack the spectrin‐binding domain, regulatory domain and part of the membrane‐binding domain. (C) Conservative analysis of the mutation site. The comparison results show that the Leu residue at 97, the missense mutation in the ANK1 protein, is well conserved across Homo sapiens, Pan troglodytes, Physeter catodon, Macaca mulatta, Mus musculus, Takifugu rubripes, Danio rerio and Xenopus tropicalis. (D) Structural change prediction of ANK1 mutants. The three‐dimensional structure of the ANK1 membrane‐binding domain (1‐827 amino acids) before and after mutation was predicted by SWISS‐MODEL. In the black box, the local structures of the site where mutation p.L97R occurs are partially enlarged; blue indicates the positively charged amino acid after mutation. Three‐dimensional structure of p.E142X, p.Y216X and p.R281X mutants indicates the incomplete structure of the domain because of the early terminated translation
