Figure 2.
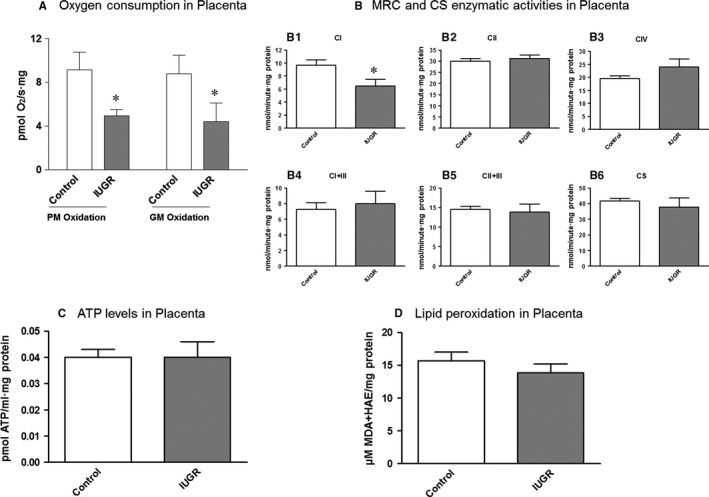
A, Oxygen consumption in placental mitochondria of the study groups. A significant decrease in MRC Complex I‐stimulated oxygen consumption (both PM and GM Oxidation) was observed in the IUGR cohort (grey bars) compared to controls (empty bars). B, Enzymatic activities of the complexes of the MRC and CS in placental tissue of the study groups. A significant decreased was observed of complex I activity in placenta from IUGR pregnancies (B1: grey bars) while other complexes (B2, B3, B4, B5) and also CS (B6) activity remained conserved. C, Total ATP levels in placental tissue of the study groups. No significant differences were observed between IUGR pregnancies (grey bars) and controls (empty bars). D, Lipid peroxidation as an indicator of oxidative damage in placental tissue of the study groups. No significant differences were evidenced in placental tissue between IUGR pregnancies (grey bars) and controls (empty bars). Results are expressed as mean ± SEM and Mann‐Whitney tests were used to seek for statistical analysis between groups. ATP, adenosine triphosphate; CI, complex I; CII, complex II; CIV, complex IV; CI + III, complex I + III; CII + III, complex II + III; CS, citrate synthase; GM oxidation, glutamate/malate oxidation; HAE, 4‐hydroxyalkenal; IUGR, intrauterine growth restriction; MDA, malondialdehyde; PM oxidation, pyruvate/malate oxidation; MRC, mitochondrial respiratory chain; * P < 0.05
