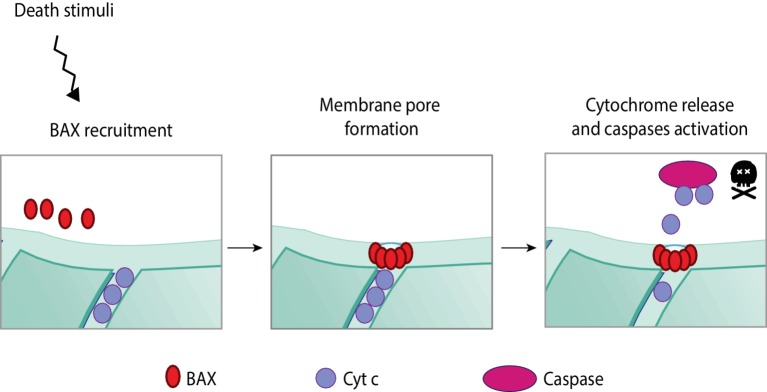
Figure 6.
Apoptotic intrinsic pathway mediated by mitochondria. The programmed and regulated cell death, apoptosis, can occur via two different pathways—intrinsic or extrinsic—according to the origin of the death stimuli, whether it is intrinsic or extrinsic to the cell. Upon intrinsic death stimuli, such as, for example, DNA damage or oncogene activation, the intrinsic apoptotic pathway is activated, which is mediated by mitochondria. Intrinsic stimuli induce the oligomerization of a pro-apoptotic BcL-2 protein—BAX. These oligomers are able to permeabilize the mitochondrial membrane by pore formation on the OMM. Membrane permeabilization allows the release of pro-apoptotic molecules from the IMS, importantly, cytochrome c. In a complex together with other pro-apoptotic proteins, cytochrome c activates caspases, the effectors of apoptosis.