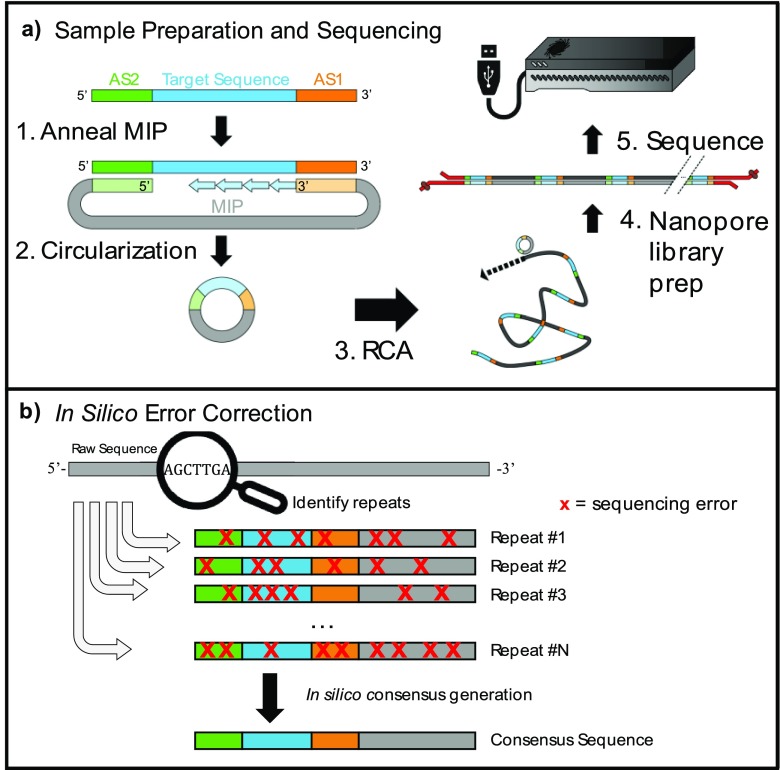
Figure 1.
Sequencing ultrashort reads on the MinION. (a) (1) Molecular inversion probes (MIPs) anneal adjacent to the target sequence (blue) at anchor site 1 (AS1, orange) and anchor site 2 (AS2, green). Phusion polymerase copies the target sequence into the MIP; the lack of 5′ → 3′ exonuclease activity ensures that extension halts when the polymerase reaches AS2. (2) Ampligase ligates the extended template to the phosphorylated 5′ end of the MIP, generating circular ssDNA. Linear ss- or dsDNA fragments are degraded by a combination of exonuclease I and exonuclease III. (3) The circular DNA is subjected to RCA to generate tandem repeats of the original target, yielding ultralong, concatemerized ssDNA. (4) The RCA product is converted to dsDNA with Taq polymerase and subjected to ONT library preparation. (5) Sequencing reads are collected from a new MinION R9.4 flow-cell run for 24 h. (b) The raw sequences are compiled and analyzed. The identified repeats have poor accuracy in isolation, but since the sequencing errors vary across repeats, they can be aligned together to produce a high-fidelity consensus sequence.