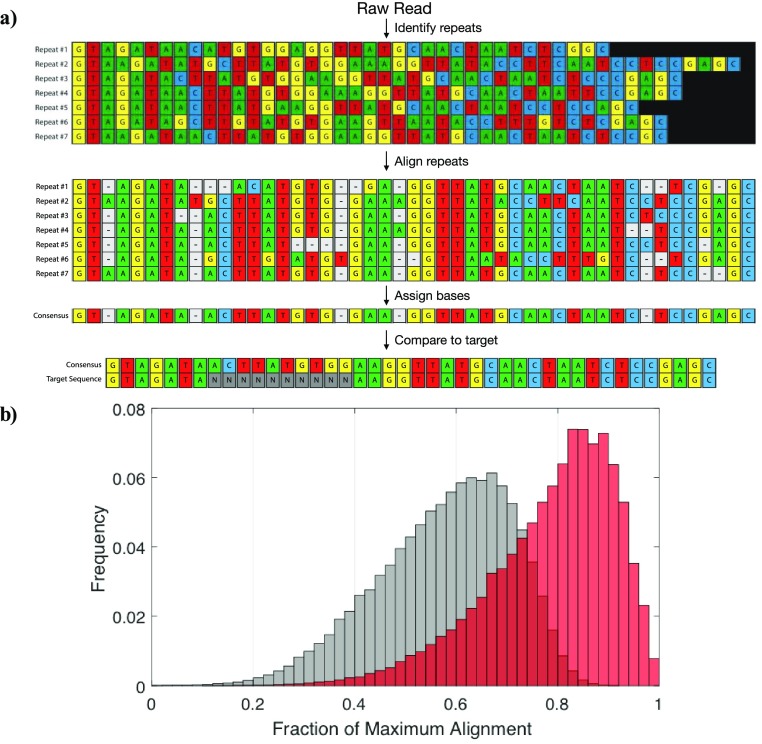
Figure 3.
Improving read accuracy through repeat-based consensus. (a) Representative consensus sequence generation. A single, base-called read is split into its individual repeats. These repeats are aligned with each other to generate a consensus sequence via a winner-take-all base-calling strategy. Gaps are removed and the consensus sequence is then compared back to the original sequence to assess the postalignment accuracy. (b) Histogram of alignment scores before (gray) and after (red) consensus sequence generation. The “before” alignment score is an average over the alignment scores of all the repeats found within a single raw read. Data includes all reads with more than three identified repeats, regardless of the quality score or pass/fail designation of the MinION software.