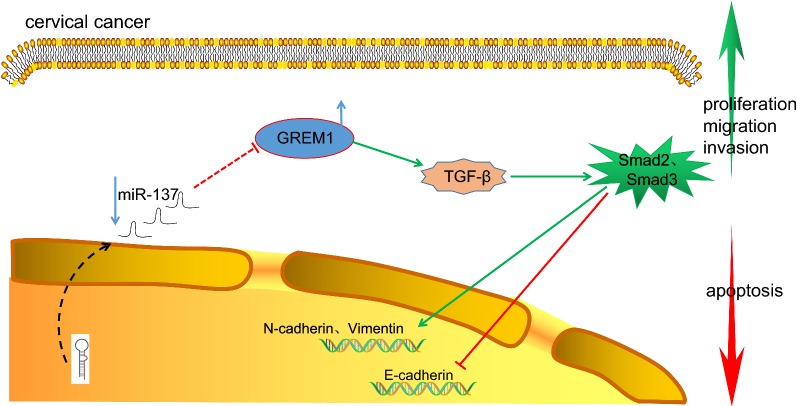
Fig. 12.
Schematic representation of the underlying mechanism of miR-137 in CC. In CC, the expression of miR-137 decreased significantly and the expression of GREM1 increased significantly. MiR-137 can target and inhibit the expression of GREM1 gene. Inhibition of miR-137 could promote the expression of GREM1, and GREM1 could promote the expression of TGF-β1, Smad2, Smad3, N-cadherin and Vimentin. Overexpression of miR-137 could inhibit the CC cell proliferation, migration and EMT while inducing apoptosis. CC cervical cancer, GREM1 gremlin-1, miR-137 microRNA-137