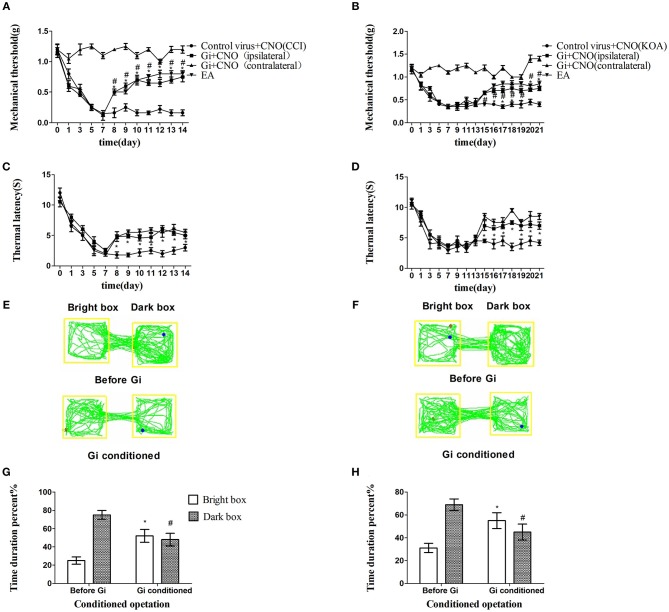
Figure 3.
Chemogenetic inhibition of GABAergic neurons in the vlPAG replicated the effects of EA. (A,B) Time course of tactile threshold in response to von Frey filaments. (C,D) The noxious heat stimulus (53°C) caused a change in the thermal thresholds. Tactile (A) and thermal (C) withdrawal thresholds changes in CCI mice after chemogenetic inhibition. Changes in tactile (B) and thermal (D) withdrawal thresholds of KOA mice caused by chemogenetic inhibition. Motion map of chemogenetic inhibition of conditioning in the CPP test with CCI (E) and KOA mice (F). G,H are summary values of motion trajectories. Virus was injected 21 days before the behavior test. CNO (1 mg/kg) was administered once a day starting from the 8th to the 14th day in the CCI model and starting from the 15th to the 21st day in the KOA model. EA (1 mA and 0.1 ms) at 2 Hz was administered for 30 min. Once a day starting from the 8th to the 14th day in the CCI model and starting from the 15th to the 21st day in the KOA model, all behavior tests were completed 2 h after CNO administration. Control groups consisted of CCI or KOA mice injected with control virus and CNO but without EA treatment. Data are expressed as means ± SEM (n = 12 in each group). In A–D, *p < 0.05, compared with control group; #p < 0.05, compared with the model group; in G,H,*p < 0.05, compared with the bright box time duration percent before chemogenetic inhibition; #p < 0.05, compared with the dark box time duration percent before chemogenetic inhibition.