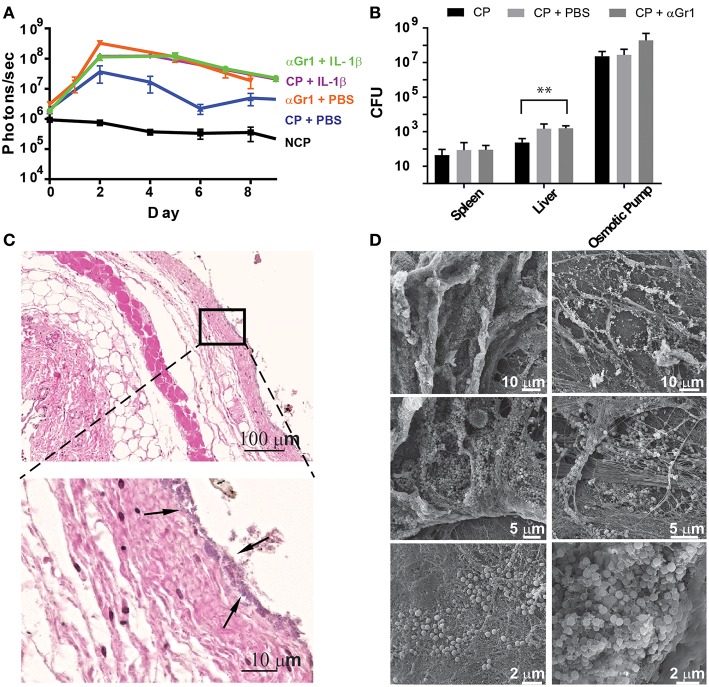
Figure 6.
Neutrophils prevent early tissue colonization by S aureus. (A) Quantification of bioluminescence of S aureus Xen29 in C57Bl/6 mice implanted with colonized osmotic pumps, filled with 100 ml of either PBS or IL-1b, with or without neutrophil depletion after anti-Gr-1 mAb application. (B) Comparison of absolute bacterial CFU counts in different organs 10 days after implanting colonized osmotic pumps (CP) with or without neutrophil depletion. Data is presented as mean±SD for 6 mice used in each experimental group during 2 independent experiments. (C) Microscopic evaluation of skin samples on day 2 after implantation of osmotic pumps colonized with S aureus Xen29 into neutrophil-depleted C57Bl/6 mice. Early colonization of skin tissue by S. aureus could be detected (arrows). (D) Representative examples of scanning electron microscopy from colonized peri-implant tissue. These images are representative for 6 mice per experimental condition. Multiple t-tests were performed with GraphPad PRISM 8 using the Holm-Sidak method, (alpha = 0.05) for comparisons between data for S. aureus colonized pumps containing PBS and all other cytokines (* p < 0.0332, ** p < 0.0021, *** p < 0.0002).