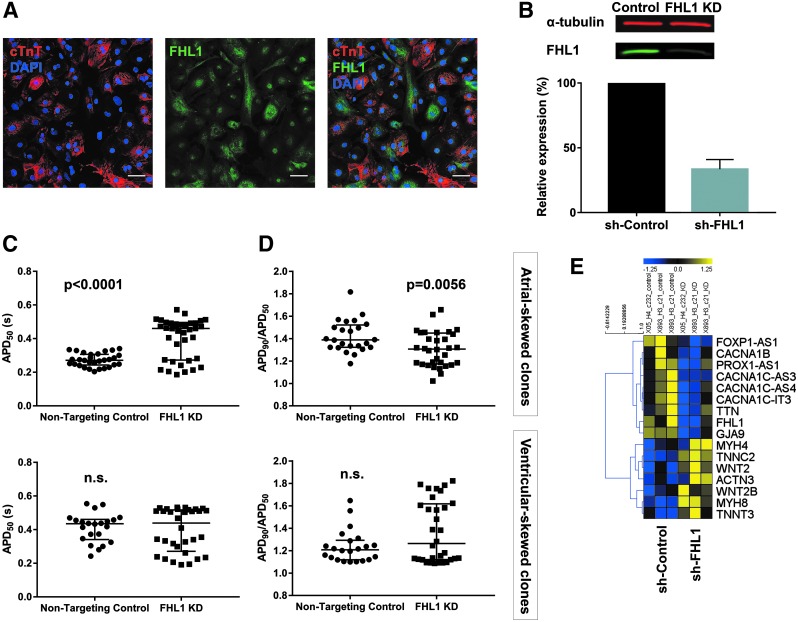
FIG. 6.
Reduced expression of FHL1 shifts hiPSC-CM AP morphologies away from atrial-like properties. (A) Immunofluorescence of cTnT and FHL1 at day 40 (representative of three analyzed clones). Scale bar represents 50 μM. (B) Representative western blot and quantification from five clones (representing three unrelated individuals) showing FHL1 knockdown efficiency via shRNA. Data are reported as mean ± SEM. (C) Cells from clones that had a mean APD90/APD50 > 1.4 in the control condition had increased APD50 with FHL1 knockdown. Data were collected from same differentiations as represented in (B). (D) Cells from clones that had a mean APD90/APD50 > 1.4 in the control condition had decreased APD90/APD50 with knockdown of FHL1. Data for (C, D) are reported as median ± the interquartile range. (E) Heatmap of differentially expressed genes from FHL1 knockdown with potential involvement in cardiomyocyte development (FOXP1-AS1, PROX1-AS1, WNT2, WNT2B) or function (electrophysiology: CACNA1B, CACNA1C-AS3, CACNA1C-AS4, CACNA1C-IT3; gap junction: GJA9; contraction: TTN, MYH4, TNNC2, ACTN3, MYH8, TNNT3). P values were calculated by either a Student's t-test or Mann–Whitney U test. shRNA, short hairpin RNA.