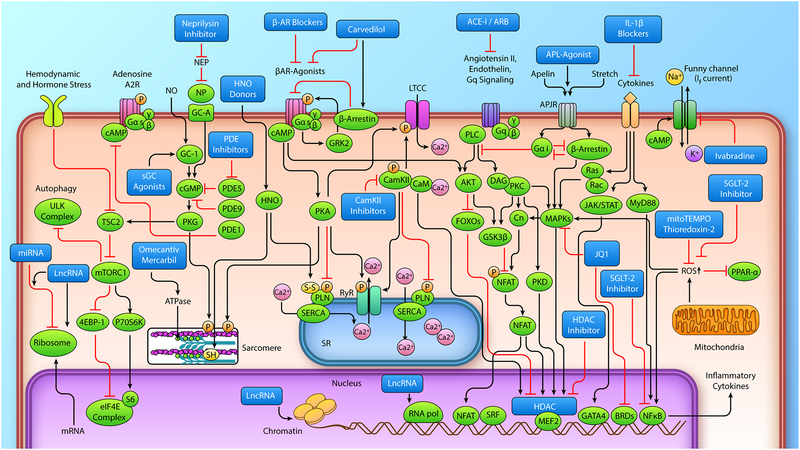
Figure 1. Myocyte signaling approaches for the treatment of Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction.
Individual therapeutic approaches are identified in the figure by the dark blue boxes. Abbreviations are: miRNA, micro ribonucleic acid; mRNA, messenger ribonucleic acid; lncRNA, long noncoding ribonucleic acid; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; TSC2, tuberous sclerosis complex-2; mTORC1, mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1; 4EBP-1, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein 1; p70S6K, ribosomal protein S6 kinase; eIF4E, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E; S6, ribosomal protein S6; ULK, UNC-51 like kinase; NO, nitric oxide; NP, natriuretic peptide; ANP, atrial natriuretic peptide; sGC, soluble guanylate cyclase; cGMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate; PDE, phosphodiesterase; PKG, protein kinase G; PKC, protein kinase C; PKD, protein kinase D; SH, thiol modification; S-S, disulfide; DAG, diacylglycerol; HNO, nitroxyl; β-AR, β-adrenergic receptor; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; GRK2, G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2; PKA, protein kinase A; PLN, phospholamban; SERCA, sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase; FOXO, forkhead box O; SR, sarcoplasmic reticulum; RyR, ryanodine receptor; LTCC, L-type calcium channel; CAMKII, calcium-calmodulin-dependent kinase II; CaM, calmodulin; ACE-I, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin II receptor blocker; APL-agonist, apelin agonist; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; GSK3-β, glycogen synthase kinase 3-β; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T cells; MAPKs, mitogen-activated protein kinase; SRF, serum response factor; MEF2, myocyte enhancer factor 2; HDAC, histone deacetylase; GATA4, GATA binding protein 4; NFκB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; RNA pol, RNA polymerase; SGL-T2 inhibitors, sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors; PPAR-α, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-α; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88; JAK, janus kinase; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; Gsα, stimulatory G protein α-subunit, Gqα, G protein-q α-subunit; PLC, Phospholipase C; P, phosphorylation modification; ROS, reactive oxygen species. (Illustration Credit: Ben Smith).