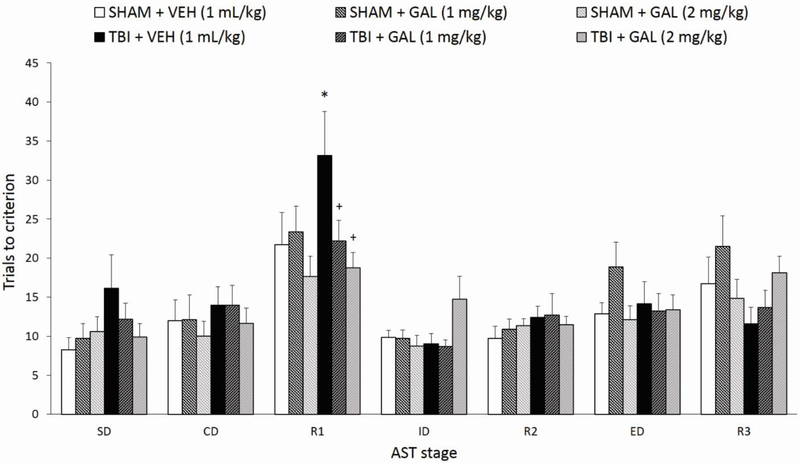
Fig. 3.
Controlled cortical impact injury impaired reversal learning on the AST compared to SHAM + VEH, manifested as an overall significantly higher number of trials to criterion, while chronic GAL treatment (1 and 2 mg/kg/day) restored cognitive performance after brain trauma. Significantly more trials were required to reach criterion during R1 (compared to all other tasks), ED (compared to SD and R2), and R3 (compared to SD, CD, ID, and R2) when rats were collapsed across groups (p’s<0.05). *p<0.05 versus SHAM + VEH group, +p<0.05 versus TBI + VEH group. Data are expressed as mean trials to criterion ± SEM (n=7-8/group). TBI, traumatic brain injury; AST, attentional set-shifting test.