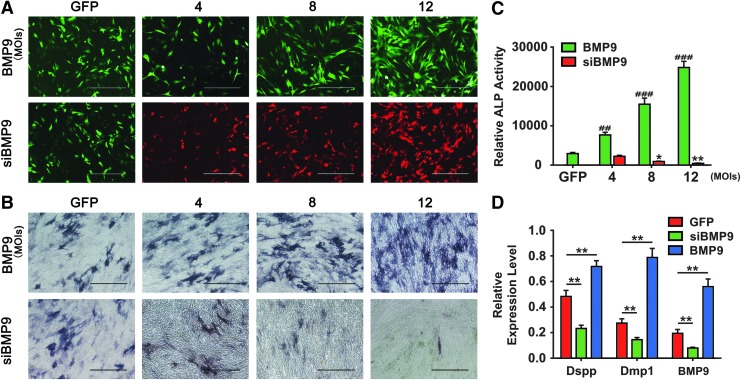
FIG. 6.
Silencing BMP9 expression decreases osteo-/odontoblastic marker expression in dental progenitor cells. (A) The GFP and RFP expression of the infected iSCAPs improved with the increased MOIs of AdBMP9 or AdsiBMP9 at 48 h after infection. The infection efficiency was indicated by the GFP or RFP expression proportion of the cells. (B) ALP histochemical staining assay. Subconfluent iSCAP cells were infected with the indicated MOIs of AdGFP, AdBMP9, or AdsiBMP9. At 5 days after infection, ALP staining assays were carried out. Representative staining results are shown. Scale bars: 400 μm. (C) Quantitative ALP assay. The iSCAPs were seeded in 24-well plates, and the treatment conditions were the same as those described in (B). #Indicated the significance between BMP9 and GFP control group, ##P < 0.01; ###P < 0.001; *shows the significance between siBMP9 and GFP control group, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. (D) Relative mRNA expression of Dspp, Dmp1, and BMP9 was determined by qPCR. Subconfluent iSCAP cells were infected with AdGFP, AdsiBMP9, or AdBMP9 for 5 days. Total RNA was isolated and subjected to reverse transcription and quantitative real-time PCR by using primers specific for mouse Dspp, Dmp1, BMP9, as well as Gapdh. The 2−ΔΔCt value was used to calculate the relative gene expression normalized by the expression level of Gapdh. Each assay condition was done in triplicate. **P < 0.01 compared with the AdGFP-infected iSCAPs control group. GFP, green fluorescent protein; RFP, red fluorescent protein; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; Dspp, dentin sialophosphoprotein; Dmp1, dentin matrix protein 1; iSCAP, immortalized mouse dental apical papilla. MOIs, multiplicities of infection; qPCR, quantitative real-time PCR. Color images are available online.