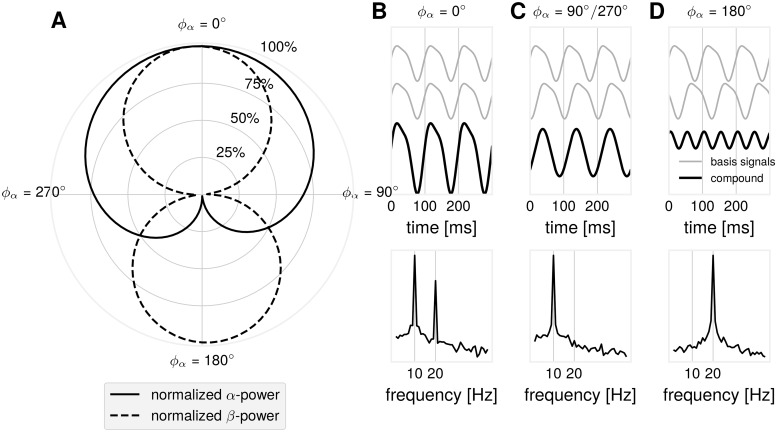
Fig 10. Illustration: Possible α/β-dynamics as function of the time delay for simple synthetic signals.
Two non-sinusoidal μ-wave signals were mixed with varying time delay ϕα between them (ϕα = 360° is equal to 100 ms, a full cycle of the base α-frequency oscillation). A full α-cycle corresponds to two full β-cycles: ϕα = 2 ⋅ ϕβ. (A) A polar plot showing α- and β-power as a function of the time delay ϕα. α- and β-power decay differentially as a function of the time delay ϕα. (B) Time course of the basis signals and the compound signal with the corresponding power spectrum showing maximal α- and β-power for ϕα = 0°. (C) Time course of the basis signals and the compound signal with the corresponding power spectrum showing attenuation of β-power for ϕα = 90°/270°. (D) In the case of ϕα = 0°, in the compound signal, only the β-component remains when the α-peaks of first basis signal align the the troughs of the second basis signal, causing cancellation.