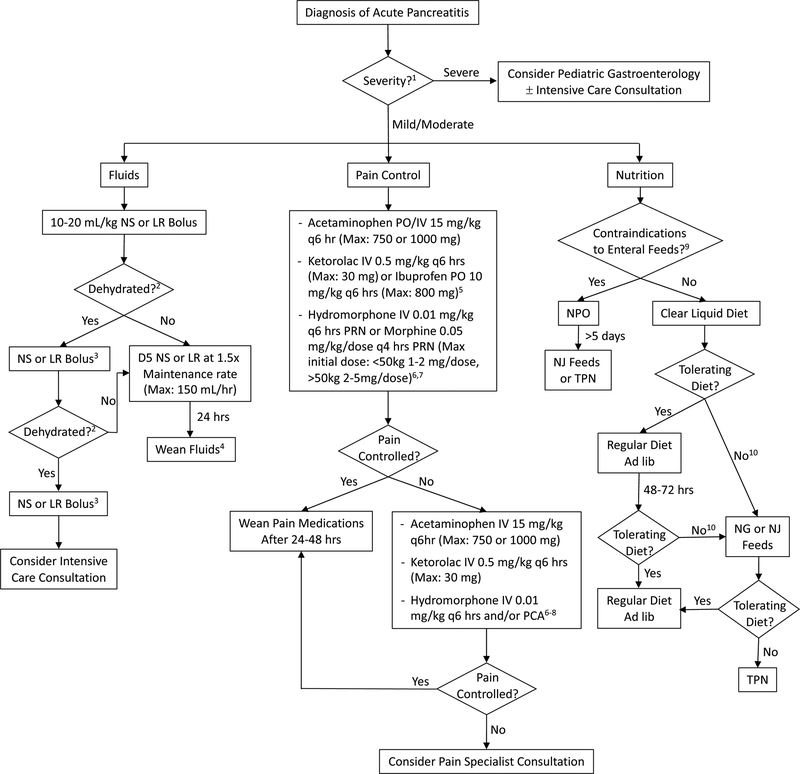
Figure 1. Treatment algorithm for pediatric AP.
Abbreviations: NS=normal saline, LR=lactated Ringers, D5=5% Dextrose, PO=per os, IV=intravenous, PRN: pro re nata (as needed), PCA: patient controlled analgesia, NPO: nil per os (nothing by mouth), NJ=nasojejunal, NG=nasogastric, TPN=total parental nutrition. 1 To help guide management, determine severity of AP (13). 2 Need for continued boluses determined by: signs of dehydration: Urine output < 1 cc/kg/hr, tachycardia, hypotension, delayed capillary refill, and poor skin turgor. Avoiding aggressive fluids and use of goal-directed fluid therapy is essential to preventing complications such as pulmonary edema. 3 10–20 mL/kg, based on clinical status. Monitor for signs of fluid overload or third-spacing. Consider LR over NS if metabolic acidosis is present. 4 Wean based on clinical status and enteral intake. 5 Use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs only if BUN and creatinine are normal. 6 Other opiates may be substituted based on patient needs and institutional preferences. 7 When using opioids, place patient on laxatives. Recommend: Polyethylene glycol 3350 1g/kg/day (divided once or twice daily) if no stools in 24–48 hrs. May increase to achieve goal of at least one soft stool daily. 8 Consult pain service when on PCA, if service available. 9 Examples of contraindications to enteral feeding include, but are not limited to: disrupted pancreatic duct, intestinal obstruction, and ileus. 10 If not tolerating adequate diet within 48–72 hrs, consider if pain and/or nausea adequately controlled. For antiemetics, recommend: IV or PO ondansetron 0.15 mg/kg/dose q6–8 hrs as needed for nausea and emesis. Maximum dose of 8 mg q8 hrs. Also consider imaging to evaluate for complications from pancreatitis (e.g. pancreatic fluid collection/necrosis or pancreatic duct stricture/stones). Recommend: IV contrast enhanced CT or MRCP if biliary/pancreatic duct abnormalities are suspected (with IV secretin if available for pancreatic duct evaluation).