Fig. 4.
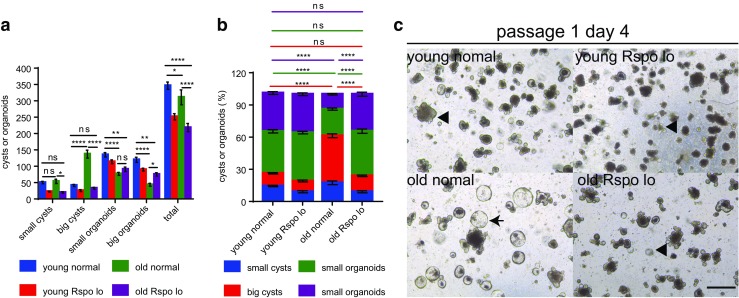
Reduction in R-spondin-1 exposure during subculture ameliorates the aging-induced deficiency in differentiation of ISCs. a-c) Cultured crypts were dissociated and passaged on day 14 after primary plating. a,b Absolute number (a) and percentage (b) of grown out structures. c Representative pictures of indicated groups on day 4 after secondary plating. Young normal: ISCs derived from young mice culturing in normal concentration of R-spondin-1; young Rspo lo: ISCs derived from young mice culturing in 1/3 concentration of R-spondin-1; old normal: ISCs derived from old mice culturing in normal concentration of R-spondin-1; old Rspo lo: ISCs derived from old mice culturing in 1/3 concentration of R-spondin-1; Small cysts: diametres≤70 μm; big cysts: diameters>70 μm; small organoids: with crypt-villus architectures, budding number ≤ 3; big organoids: with crypt-villus architectures, budding number > 3. Arrow heads indicate typical organoids; arrows indicate typical big cysts. Data are displayed as mean ± SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001. ns, not significant. Two-way ANOVA analysis was used. Scale bar: 200 μm
