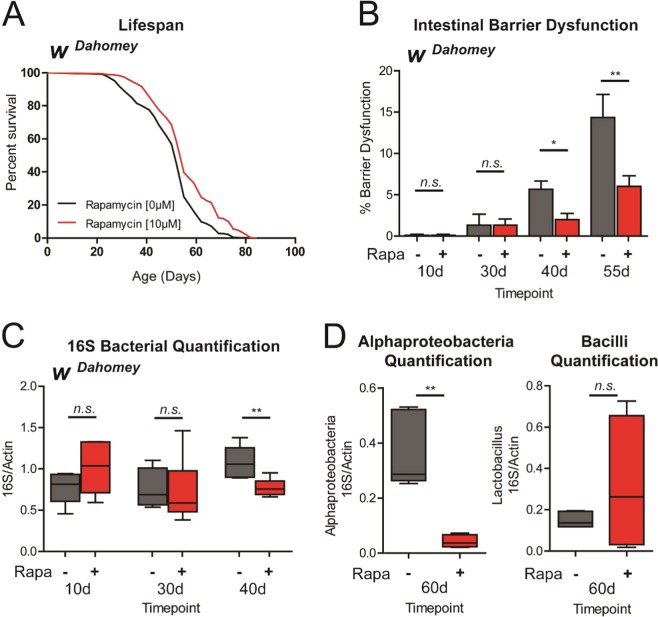
Figure 1.
Rapamycin treatment improves gut health and modulates microbiota composition during aging. (A) Survival curves of wDahomey females with or without rapamycin treatment from day 4 onwards (post-eclosion). p < 0.0001, log rank test; n > 225 flies. Representative result of 4 separate lifespan trials. (B) Intestinal integrity during aging of wDahomey females with or without rapamycin treatment from day 4 onwards (post-eclosion). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA/Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test; n = 300 flies on day 10 per treatment. (C) Bacterial levels assayed by qPCR of the 16S rRNA gene in surface sterilized, non-smurf wDahomey females with or without rapamycin treatment from day 4 onwards (post-eclosion). **p < 0.01, Mann-Whitney U-test; n = 6 replicates of five flies per timepoint. (D) Bacterial levels assayed by taxon specific primers in surface sterilized, non-smurf wDahomey females fed with or without rapamycin from day 4 onwards. **p < 0.01, Mann-Whitney U-test; n = 6 replicates of five flies per timepoint. Rapamycin was provided in the media at a concentration of 10 μg/ml for (A–D). All error bars represent SEM.