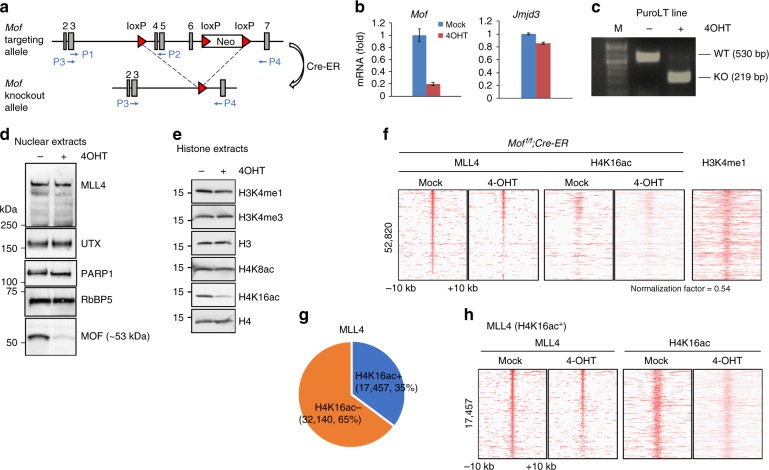
Fig. 4.
A subset of MLL4-bound genomic regions overlaps with H4K16ac. SV40T-immortalized Moff/f;Cre-ER brown preadipocytes were treated with 4-hydroxytamoxifen to delete Mof. Cells were collected for reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR), western blot and chromatin immunoprecipitation–sequencing (ChIP-Seq) analysis. a Schematics of targeting allele and knockout allele of Moff/f mice. In the targeting allele, a single loxP site was inserted in the intron before exon 4 and a neomycin selection cassette flanked by loxP sites was inserted in the intron after exon 6. The locations of RT-PCR primers P1–P2 (used in Fig. 4b) and P3–P4 (used in Fig. 4c) are indicated by arrows. b Quantitative RT-PCR confirmation of Mof deletion in preadipocytes. The data are presented as mean ± s.d. Two technical replicates from a single experiment were performed. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. c RT-PCR confirmation of wild-type and truncated Mof mRNA. d Western blot analysis of MLL4, UTX, and MOF. PARP1 and RbBP5 were used as loading controls. e Western blot analysis of histone modifications (also see Supplementary Fig. 15). f Heat maps around MLL4-binding sites. H4K16ac ChIP-Seq data were normalized with global H4K16ac levels measured by western blot. Published H3K4me1 data were obtained from GEO database (GSE74189)49. g Pie chart illustrating that 35% of MLL4-binding sites overlap with H4K16ac. h Heat maps of MLL4 and H4K16ac around 17,457 H4K16ac+ MLL4-binding sites