Fig. 6.
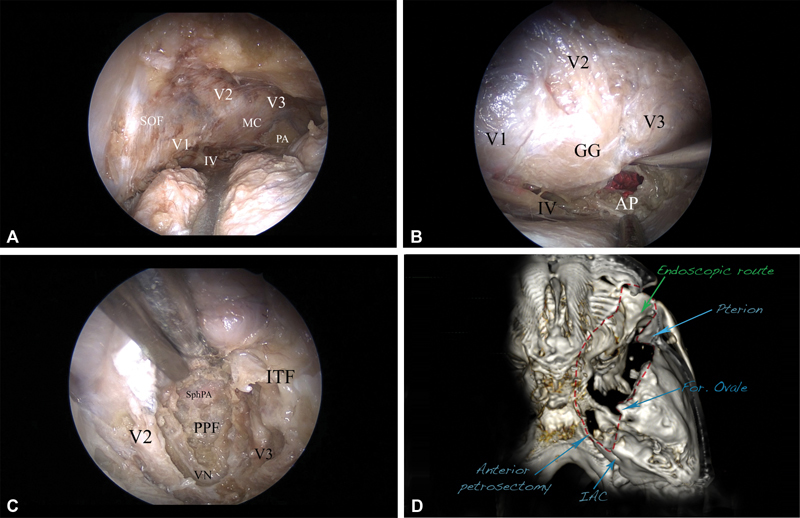
The posterolateral route and exposure to the posterior fossa, right side. ( A ) The whole cavernous sinus is seen, including the Meckel's cave (MC), V1, V2, V3, and IV cranial nerves, as well as the petrous apex (PA). ( B ) The mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve is elevated, and the anterior petrosectomy (AP) is done, exposing the corridor of the posterior fossa. The dura is incised, and the pons, as well as the trigeminal nerve, is seen. ( C ) The inferior route (light blue, Fig. 4B ), exposing the pterygopalatine fossa (PPF) and the infratemporal fossa (ITF). The bone between V2 and V3, as well as the floor of the middle cranial fossa, is removed, completely unroofing V2 and V3 and thus opening access to the PPF and the ITF. The vidian nerve (VN), as well as the vidian canal, are revealed. The sphenopalatine artery (SphPA) is seen in the PPF. ( D ) Postoperative computed tomography (CT) scan-based three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction presenting the area of bone removal (red dashed line), corresponding to the exposure to the posterior fossa (anterior petrosectomy) and to the infratemporal fossa (temporal fossa floor removal). 3D reconstruction using the OsiriX software (version 5.8.1, Pixmeo, Bernex, Switzerland). Abbreviations: AP, anterior petrosectomy; ITF, infratemporal fossa; MC Meckel's cave; PA, petrous apex; PPF, pterygopalatine fossa; SphPA, sphenopalatine artery; VN, vidian nerve.
