Figure 2.
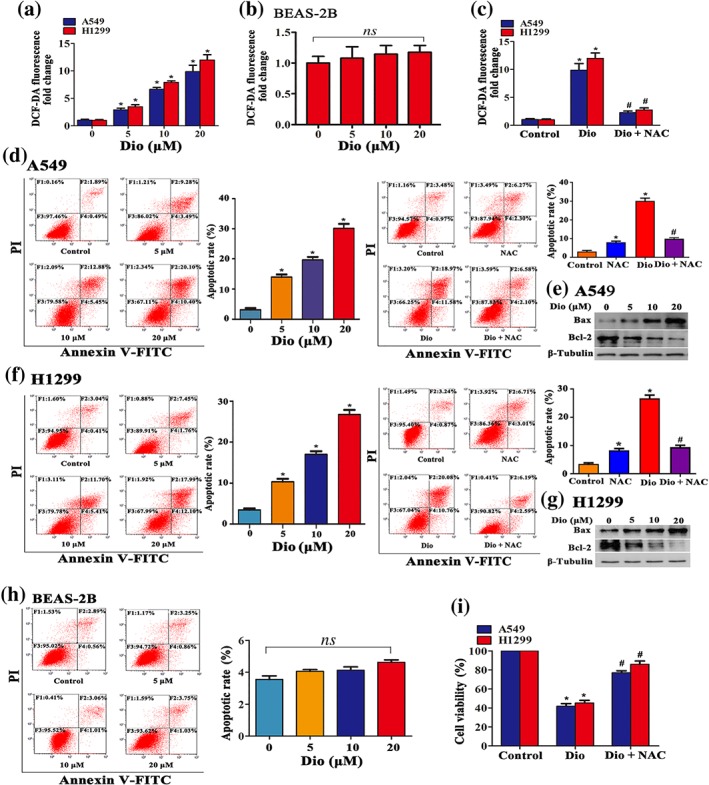
Diosmetin (Dio) induces cell apoptosis via cellular ROS accumulation. The effect of diosmetin at the indicated concentrations on ROS production in A549 and H1299 cells (a) and BEAS‐2B cells (b). (c) ROS accumulation blocked by administration of an ROS scavenger NAC (25 mM ) examined by DCF‐DA fluorescence assay. Data shown are means ± SD; n = 5. *P < 0.05, significantly different from control group; # P < 0.05, significantly different from Dio alone. The effect of diosmetin (5 to 20 μM) treatment for 12 hr on A549 (d) and H1299 (f) cells apoptosis. Administration of NAC (25 mM) reversed the effect of diosmetin (20 μM) on cell apoptosis determined by flow cytometry. Data shown are means ± SD; n = 5. *P < 0.05, significantly different from control group. # P < 0.05, significantly different from Dio. (e, g) Diosmetin (5 to 20 μM) promoted Bax and suppressed Bcl‐2 expression in A549 and H1299 cells analysed by Western blotting after 12‐hr incubation. (h) The effect of diosmetin (5 to 20 μM) treatment for 12 hr on BEAS‐2B cell apoptosis determined by flow cytometry. Data shown are means ± SD; n = 5. ns, not significant. Administration of NAC (25 mM) efficiently reversed the effect of diosmetin (20 μM) on viability of A549 and H1299 cells, determined by MTT (i). Data shown are means ± SD; n = 5. *P < 0.05, significantly different from control group. # P < 0.05, significantly different from Dio. PI: propidium iodide
