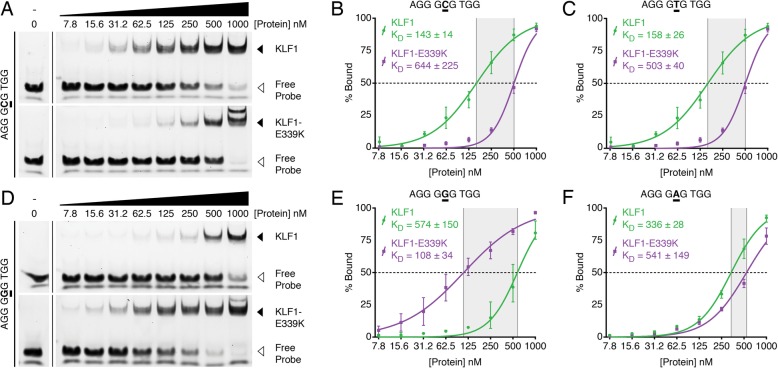
Fig. 3.
KLF1-E339K binds with strong affinity to an altered recognition sequence. a Saturation fluorescent gel shift assay of KLF1-zf and KLF1-E339K-zf (0–1000 nM) binding to a 2 nM probe representing the sequence at the Alas2 enhancer binding site (AGG GCG TGG; C5). b Free versus bound probe were quantified and plotted from replicate gel shift assays to calculate the binding affinity constant (KD) of KLF1 (green) and KLF1-E339K (purple) to the Alas2 enhancer binding site (AGG GCG TGG; C5). Curves were fit individually using with Hill Slope. Averaged KD and its standard error are reported (n = 3). c, e, f Free versus bound probe were quantified and plotted from replicate (n = 3) gel shift assays as in A) with alternate probe sequences as indicated. d Saturation fluorescent gel shift assay of KLF1-zf and KLF1-E339K-zf (0–1000 nM) binding to a 2 nM probe representing an altered sequence at the Alas2 enhancer binding site (AGG GGG TGG; G5)