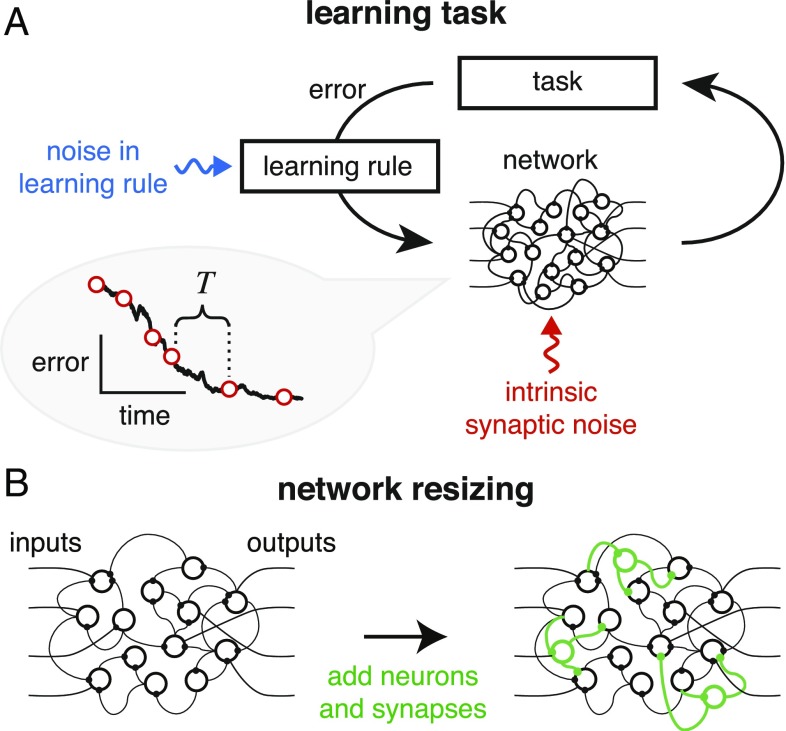
Fig. 1.
(A) Schematic of learning in a neural network. Information on task error is received by a learning rule which converts this information into synaptic changes that decrease task error. Biologically, the learning rule faces several challenges: It will be subject to noise and perturbations (blue arrow), and the synapses themselves may suffer from intrinsic noise (red arrow). Error information will be acquired only intermittently, as shown in the learning curve on the left, where specifies the intermittency of feedback (main text). (B) We analyze the effect of network size on learning performance by adding redundant neurons and synapses (green) to an existing network.