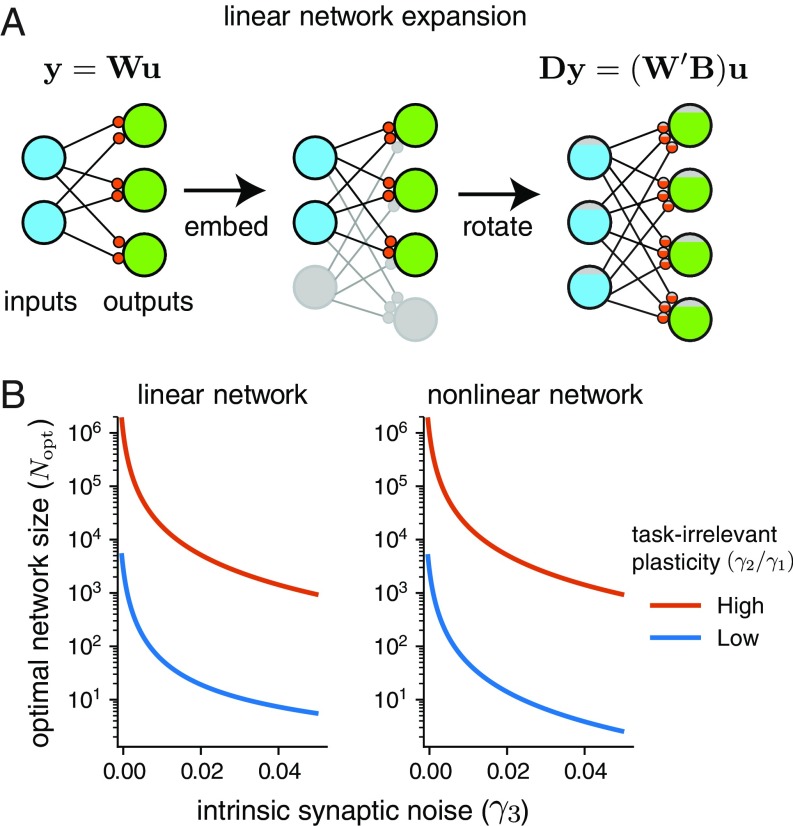
Fig. 5.
Optimal network size for linear and nonlinear networks in the presence of intrinsic synaptic noise. (A) Network expansion for a linear network, given by an embedding into a larger network, followed by a rotation of the weight matrix. This corresponds to transforming inputs by a projection and outputs by a semiorthogonal mapping . (B) Plots show the dependence of in linear and nonlinear networks using Eqs. 17 and 19. In both cases the learning rule has and . Low task-irrelevant plasticity corresponds to , while high task-irrelevant plasticity corresponds to .