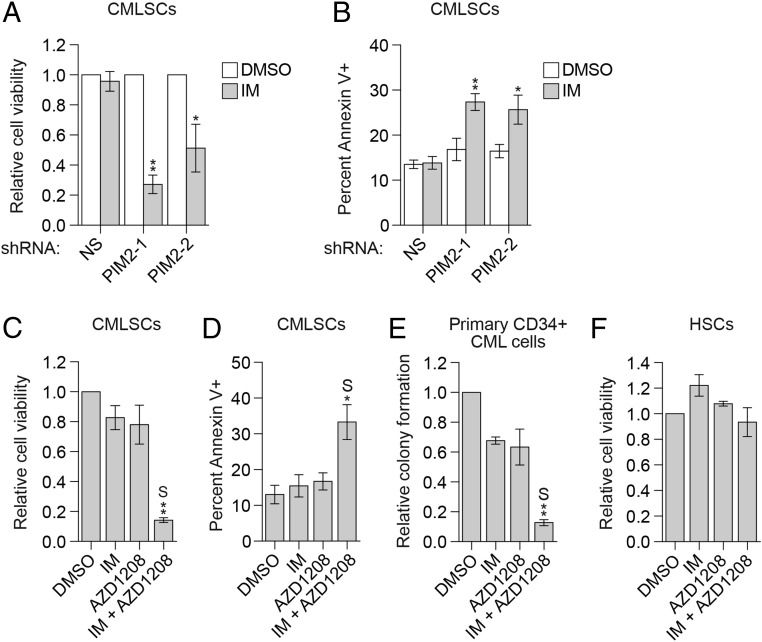
Fig. 3.
Combined treatment with IM and the PIM inhibitor AZD1208 synergistically increases the apoptosis of CMLSCs and suppresses colony formation. (A and B) Relative cell viability (A) and apoptosis (B) of CMLSCs (CD34+CD38−CD90+) from CML patient samples expressing an NS or PIM2 shRNA and treated with DMSO or IM. In A, the results were normalized to those obtained in DMSO-treated cells, which was set to 1. Error bars indicate SEM. n = 4 biological replicates. (C and D) Relative cell viability (C) and apoptosis (D) of CMLSCs (CD34+CD38−CD90+) from CML patient samples treated with DMSO, IM, AZD1208, or both IM and AZD1208. Error bars indicate SEM. n = 4 biological replicates. (E) Colony-formation assay of human primary CD34+ CML cells treated with DMSO, IM, AZD1208, or both IM and AZD1208. To perform synergy analysis, the data from four individual CML patients (shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S9G) were combined and normalized by setting DMSO treatment to 1. Error bars indicate SEM. n = 4 biological replicates. (F) Relative cell viability of normal HSCs from healthy donors treated with DMSO, IM, AZD1208, or both IM and AZD1208. Error bars indicate SEM. n = 3 biological replicates. S denotes the combined drug treatment was synergistic. *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01.