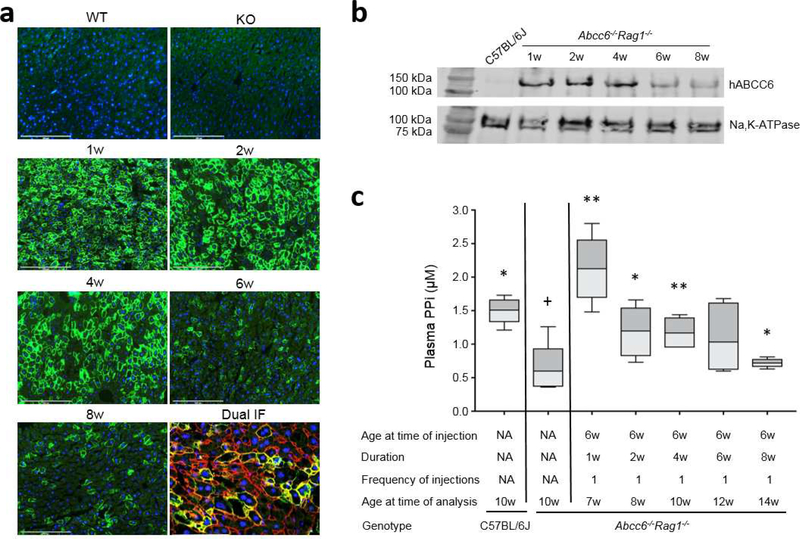
Figure 2. Administration of recombinant adenovirus revealed temporal ABCC6 expression and increase of plasma PPi in Abcc6−/−Rag1−/− mice.
A total of 25 Abcc6−/−Rag1−/− mice were administered a single injection of 4×108 IFU of Ad5-CMV-hABCC6 at 6 weeks of age. The mice were analyzed at 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8 weeks after injection. (a) Immunofluorescent labeling of human ABCC6 revealed peak response at 1 week and sustained expression up to 4 weeks (Green). Dual immunofluorescent labeling with human ABCC6 (Green) and Na,K-ATPase (Red) revealed co-localization in the basolateral plasma membrane of hepatocytes. Expression was not noted in the wild type C57BL/6J (WT) and Abcc6−/−Rag1−/− (KO) mice for human ABCC6 protein. Scale bar, 0.2 mm. Blue = DAPI. (b) Quantitation of ABCC6 protein in mouse liver by Western blot. A plasma member marker, Na,K-ATPase, served as internal control. Note negative expression of human ABCC6 in the liver of wild type C57BL/6J mice. (c) Administration of Ad5-CMV-hABCC6 resulted in increased plasma PPi at 1 week which persisted up to 6 weeks. n = 4 – 6 mice per group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, compared to Abcc6−/−Rag1−/− control mice. +p < 0.05, ++p < 0.01, compared to C57BL/6J control mice.