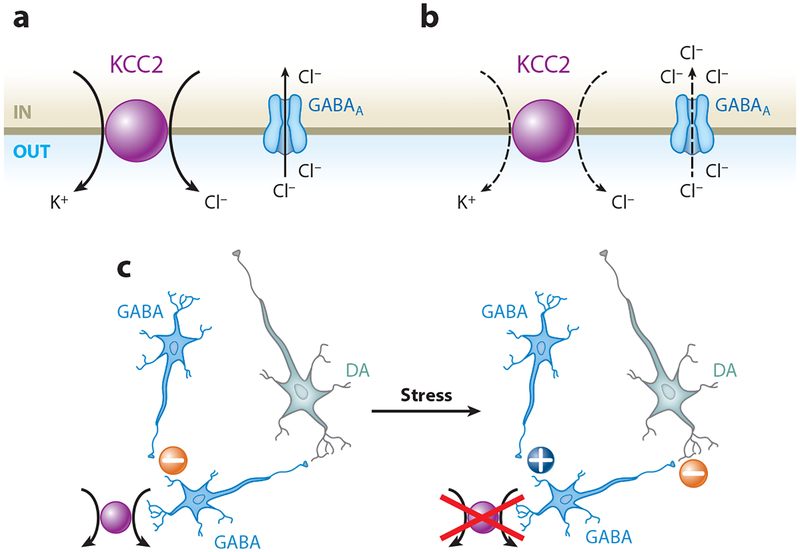
Figure 2.
Functional expression of the K+-Cl− cotransporter (KCC2) regulates neural circuitry in the ventral tegmental area (VTA). (a) KCC2 mediates Cl− extrusion from neurons, maintaining the concentration gradient that favors Cl− entry through the GABAA receptor. (b) Decreased KCC2 function leads to intracellular Cl− accumulation, resulting in an impaired Cl− gradient and decreased synaptic GABAA receptor inhibition. (c) KCC2 mediates normal GABAergic inhibition of VTA GABA neurons projecting onto dopamine (DA) neurons (left minus sign). Exposure to stress downregulates KCC2 and shifts GABAA receptor signaling toward excitation of VTA GABA neurons (plus sign). Excitation of VTA GABA neurons promotes inhibition of DA neurons (right minus sign) (11).